
A recent review by the National Psoriasis Foundation's medical board suggests that adults with psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis (PsA) may use dietary interventions to supplement standard medical therapies to reduce disease severity.

A recent review by the National Psoriasis Foundation's medical board suggests that adults with psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis (PsA) may use dietary interventions to supplement standard medical therapies to reduce disease severity.

Adalimumab trials in psoriasis show no new safety signals in nearly 5,500 patient-years (PYs) of exposure, shows a review in the British Journal of Dermatology.

The superiority of risankizumab over ustekinumab and placebo in two phase three psoriasis trials supports the value of targeting interleukin (IL)-23 alone over IL-12 and IL-23, according to study authors. The publication appeared online in the August issue of The Lancet.

Biologic efficacy may not wane under previous exposure to biologic treatments, study shows.

A review of complementary and alternative medicines used by more than 51 percent of patients with psoriasis, shows that indigo naturalis, curcumin, dietary modification, fish oil, meditation, and acupuncture may be effective in some patients, but proceed cautiously investigators say.

Patients who achieve complete skin clearance of psoriasis experience a noticeable difference in quality of life and work productivity.

Ortho Dermatologics announced in August that it resubmitted a new drug application to the FDA for DUOBRIITM1, a lotion for the treatment of plaque psoriasis.
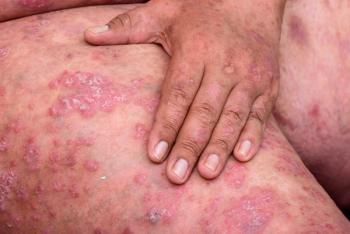
In this slideshow, we highlight some of this year's clinical advances in psoriasis and plaque psoriasis.

A JAMA Dermatology study shows that adherence to a Mediterranean diet high in anti-inflammatory nutrients may lessen psoriasis severity.

The prevalence of psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis worldwide appears to be around 20 percent, shows a meta-analysis published in JAAD.

Longer, more in-depth consultations with dermatologists, nursing staff, physician assistants could improve outcomes in psoriasis.

Obesity appears to be an important independent risk factor for children with psoriasis who go on to develop cormorbidities, such as hypertension and diabetes, a study shows.

As dermatologists become increasingly aware of comorbidities associated with psoriasis, questions of associated malignancy risk remain. Dr. Megan Noe emphasizes the need for skin cancer checks.

Patients with psoriasis have a higher risk of developing new onset diabetes mellitus. It’s a risk that’s been described as statistically significant. So, in this article, we examine dermatologic care for diabetic foot infections.

Newer biologics that target interleukin (IL)-17 and IL-23 are changing the paradigm for psoriasis treatment, report physicians.

The August issue of Dermatology Times includes a supplement edition that focuses on a patient-centered approach in psoriasis management, including an article on the importance of longer consults in the doctor's office and recommendations for individualized therapy. Read more here.

For psoriasis in difficult locations including the scalp, palms and soles, guselkumab outperformed adalimumab and placebo, shows a study published online in JAMA Dermatology.
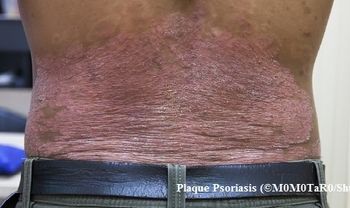
Ustekinumab has a higher drug survival rate than adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab, confirms a study of plaque psoriasis patients published in the Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery.

A new methotrexate usage survey shows that most patients with arthritis do not discuss medication modification strategies with their doctors.
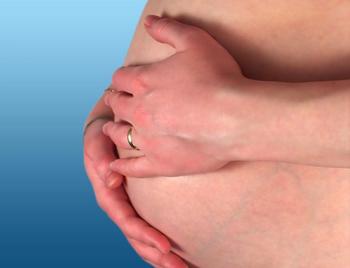
Reproductive age women with psoriasis could benefit from an endocrinologist or obstetrician referral before starting systemic therapy.

Gestational diabetes, gestational hypertension and pre-eclampsia are higher in women with psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis.

A new study advises selecting biologic therapies for psoriasis based on individual factors such as patients' comorbidities, preferences and clinical situation, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of particular biologic treatments.

This is the first time an IL-23 blocking drug has been shown to improve signs and symptoms of psoriatic arthritis.

Adalimumab may be effective for plaque psoriasis, but not heart disease and other inflammatory conditions associated with the condition. This study confirms that the inflammatory process is unique and that one treatment may not apply to other inflammatory conditions.
