Positive results in melanin, erythema, wrinkles, texture, and periorbital dermal thickness were observed during the 8-week study.

Positive results in melanin, erythema, wrinkles, texture, and periorbital dermal thickness were observed during the 8-week study.

Investigators observed lowered MASI and PGA scores in the side of the face treated with BoNT-A.

With further research, plants such as licorice, tomato, and parsley, could eventually be promising alternatives for melasma patients.

Patients treated with radiofrequency microneedling and Cysteamine cream saw significant improvement in melasma severity and skin texture.

The novel clinical trial compared the AAK cream to triple combination cream in treating patients with melasma.
The study highlights the need for personalized treatments, suggesting that this combination therapy is most beneficial when tailored to individual risk profiles.

Study participants in the treatment group experienced an observable and significant decrease in melanin index scoring.

Researchers compared the potent depigmenting agent with modified Kligman's formula, considered the gold standard therapy for melasma.
Investigators also developed a MELASQoL model using 4 predictors of quality of life impacts in patients with melasma.

A study found that a triple combination cream containing isobutylamido-thiazolyl-resorcinol, retinoic acid, and dexamethazone proved to be effective in treating melasma.

Click here to answer this week's melasma poll.
Researchers noted that serum levels of malondialdehyde and vitamin C are indicators of the impairment caused by systemic oxidative stress.

Compared to patients without melasma, blue light irradiation caused minimal changes in patients with melasma.

A split-face study found that combination therapy proved more efficacious than microneedling alone.

Researchers say the treatment, which is known to treat pigmented disorders, is also effective in treating periorbital wrinkling.
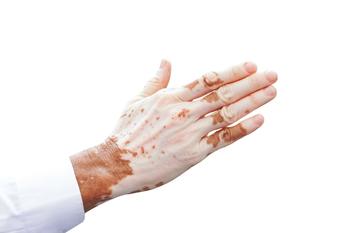
In this first part of our coverage of “The Skin of Color Update Pre-Conference Virtual Symposium” held August 3, we review challenging cases of melasma, vitiligo, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation in skin of color patients.
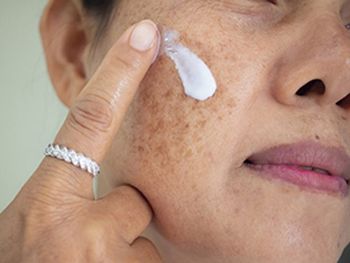
An array of agents for blocking visible light and lightening skin are joining the armamentarium to treat melasma. Despite this expanding number of therapeutic interventions, melasma is a chronic, therapeutically challenging disease for which there is no cure, so treatment plans should address both management of the disease and patient expectations.
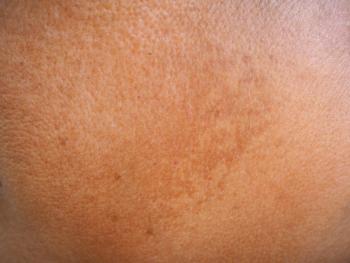
Findings from two recent pilot studies suggest 1927 nm fractional thulium fiber laser-assisted topical tranexamic acid delivery is a safe, effective melasma treatment option.

Dermatologists should consider assessing melasma patients for increased vascularity and include antivascular treatments to improve outcomes among patients whose lesions have a vascular component.

Cysteamine cream and tranexamic acid mesotherapy demonstrated similar efficacy but yielded different safety results when being compared as a treatment for melasma, according to a recently published study.

Lasers typically used for tattoo removal are on the rise as a possible treatment for melasma, with the novel 730 nm picosecond laser (PicoWay, Candela) being the most recently studied device which showed to be safe and effective for treating benign pigmented lesions.
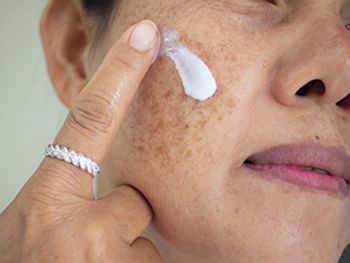
The importance of blocking visible light in the treatment of pigmentary disorders is becoming clearer. One expert says photoprotection in patients with pigmentary conditions is a therapeutic cornerstone.

Effective treatment first requires accurate diagnosis, one expert says. He offers tips to distinguish melasma from other disorders and suggests some patients may need to be checked for diabetes and metabolic syndrome if they exhibit certain presentations.

In a study of more than 200 men and women, clinicians scored patients’ pigmentation taking into account how much of the face was impacted and compared scores to patients’ responses to the Skindex-16 questionnaire.

Researchers examined a group of adult women diagnosed with melasma who applied a traditional medicinal product on one side of their face and 4% hydroquinone on the other side.