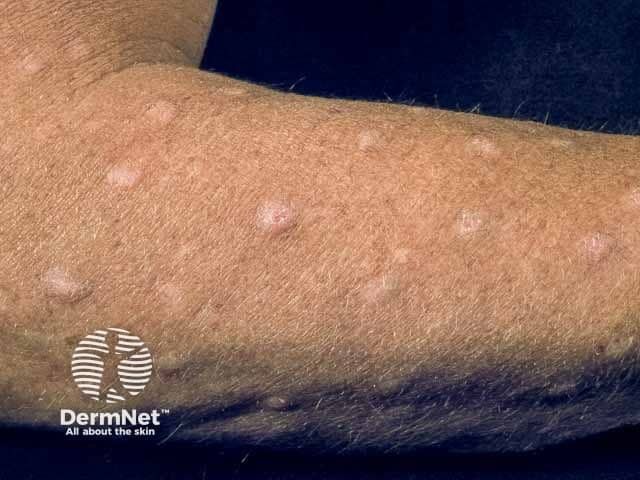
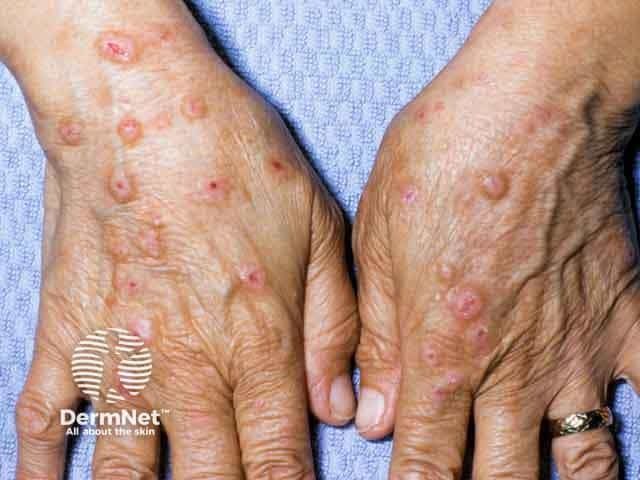
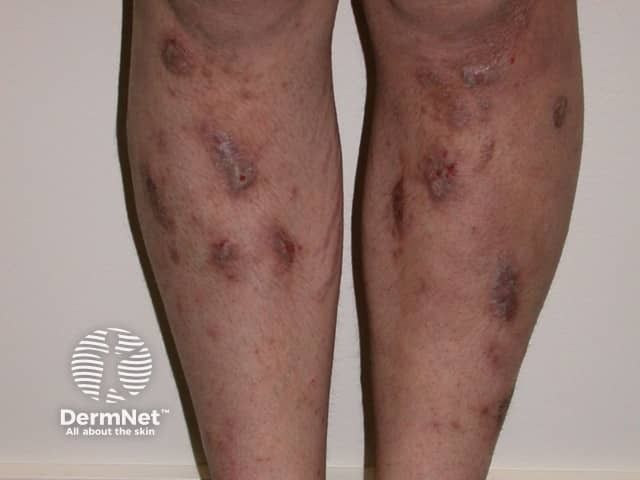
Prurigo Nodularis
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

Nearly all injection site reactions among patients in the ARCADIA 1/2 and OLYMPIA 1/2 clinical trials were mild and transient in nature.

Colleagues, mentors, and patients gathered to discuss Kwatra’s immense achievements throughout his career and the milestones that led to his endowed position.

Tofacitinib showed promise for easing itch and skin symptoms in prurigo nodularis, though effects may lessen over time.

Targeting type 2 cytokines with monoclonal antibodies has revolutionized treatment for inflammatory skin diseases, reducing symptoms and improving quality of life.

Brian S. Kim, MD, FAAD, shares itch research updates at the AAD Annual Meeting.
TJ Chao, MPAS, PA-C, discusses how to approach conversations with patients about starting systemic therapy for prurigo nodularis, emphasizing the importance of setting realistic treatment expectations, promoting long-term adherence, and providing tips for managing biologic agents administered on a bimonthly or monthly basis.

85% of Chinese PN patients saw a PP-NRS improvement of ≥ 4 points after 12 weeks of treatment.

A panelist discusses how the advent of targeted systemic therapies such as dupilumab and nemolizumab has transformed the treatment landscape for prurigo nodularis, offering more effective options for breaking the itch-scratch cycle while maintaining favorable safety profiles compared with traditional systemic treatments.

A panelist discusses how this patient's history of chronic kidney disease, diabetes, and psychological stress are significant contributing factors to his prurigo nodularis, necessitating a comprehensive treatment approach that addresses both the underlying conditions and the itch-scratch cycle.

TJ Chao, MPAS, PA-C, discusses how systemic treatments for prurigo nodularis are considered for patients with moderate to severe disease, highlighting key patient-specific factors such as comorbidities and disease severity when initiating treatment.

A panelist discusses how diagnostic differentiation of prurigo nodularis requires careful examination of the characteristic firm, hyperkeratotic nodules and consideration of the patient's history of chronic pruritus and scratching behavior, while noting that comorbid atopic dermatitis may influence treatment selection toward dual-targeting therapies.

As 2024 comes to a close, Dermatology Times is taking a look back at the studies, therapies, and advances in prurigo nodularis this year.

A panelist discusses how the treatment landscape for prurigo nodularis (PN) has evolved from primarily using topical therapies and off-label systemic medications to incorporating FDA-approved targeted biologics such as dupilumab and nemolizumab, which have demonstrated significant efficacy in reducing both the itchiness and nodular lesions.

A panelist discusses how prurigo nodularis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that disproportionately affects middle-aged adults and those with immune disorders, causing intensely pruritic nodules that significantly impact quality of life through both physical discomfort and psychological distress.

TJ Chao, MPAS, PA-C, discusses how treatment goals for prurigo nodularis should be based on disease severity and comorbidities, with adjustments to the treatment approach to optimize patient outcomes.

A collection of clinical insights on prurigo nodularis, exploring awareness and educational efforts as well as trends in treatment.

Increased awareness for prurigo nodularis may help to usher in a new era of timelier and more targeted treatment.

Melodie Young, MSN, A/GNP-C, discusses how clinical and practical considerations, such as disease severity, patient preferences, and comorbidities, should guide the selection of treatment for prurigo nodularis, and emphasizes the importance of educating patients about the role of systemic therapies, addressing their concerns, and improving awareness of available treatment options.

Melodie Young, MSN, A/GNP-C, discusses how the FDA-approved systemic treatments for prurigo nodularis, dupilumab and nevolizumabnemolizumab, differ in their mechanisms of action—dupilumab targeting IL-4 and IL-13, and nevolizumabnemolizumab targeting IL-31—and highlights their similar efficacy in reducing pruritus and lesion size, while also considering differences in safety profiles and treatment considerations.

Melodie Young, MSN, A/GNP-C, discusses how to effectively communicate with patients about managing itch in prurigo nodularis, offering practical tips such as setting realistic expectations, emphasizing the importance of consistent skin care routines, and exploring both pharmacologic and non-pharmacologic strategies to alleviate discomfort.

Melodie Young, MSN, A/GNP-C, discusses how diagnosing prurigo nodularis can be challenging due to its similarity to other pruritic conditions, and highlights the importance of recognizing key features and patient subtypes with increased prevalence to accurately differentiate it from conditions like eczema and psoriasis.

Melodie Young, MSN, A/GNP-C, discusses how prurigo nodularis imposes a significant physical and mental burden on patients, with chronic itching, skin lesions, and emotional distress leading to a reduced quality of life and increased anxiety and depression.

Data from Galderma's OLYMPIA 1 trial was recently published in JAMA Dermatology.
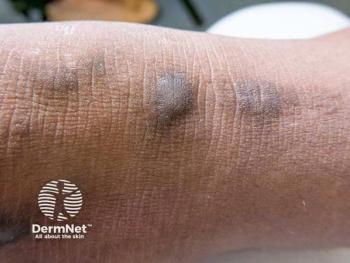
Patients treated with dupilumab saw substantial healing, with over 70% achieving >50% lesion improvement in 24 weeks.

A study showed NB-UVB phototherapy effectively reduced prurigo nodularis symptoms, with 80% of patients achieving full response.