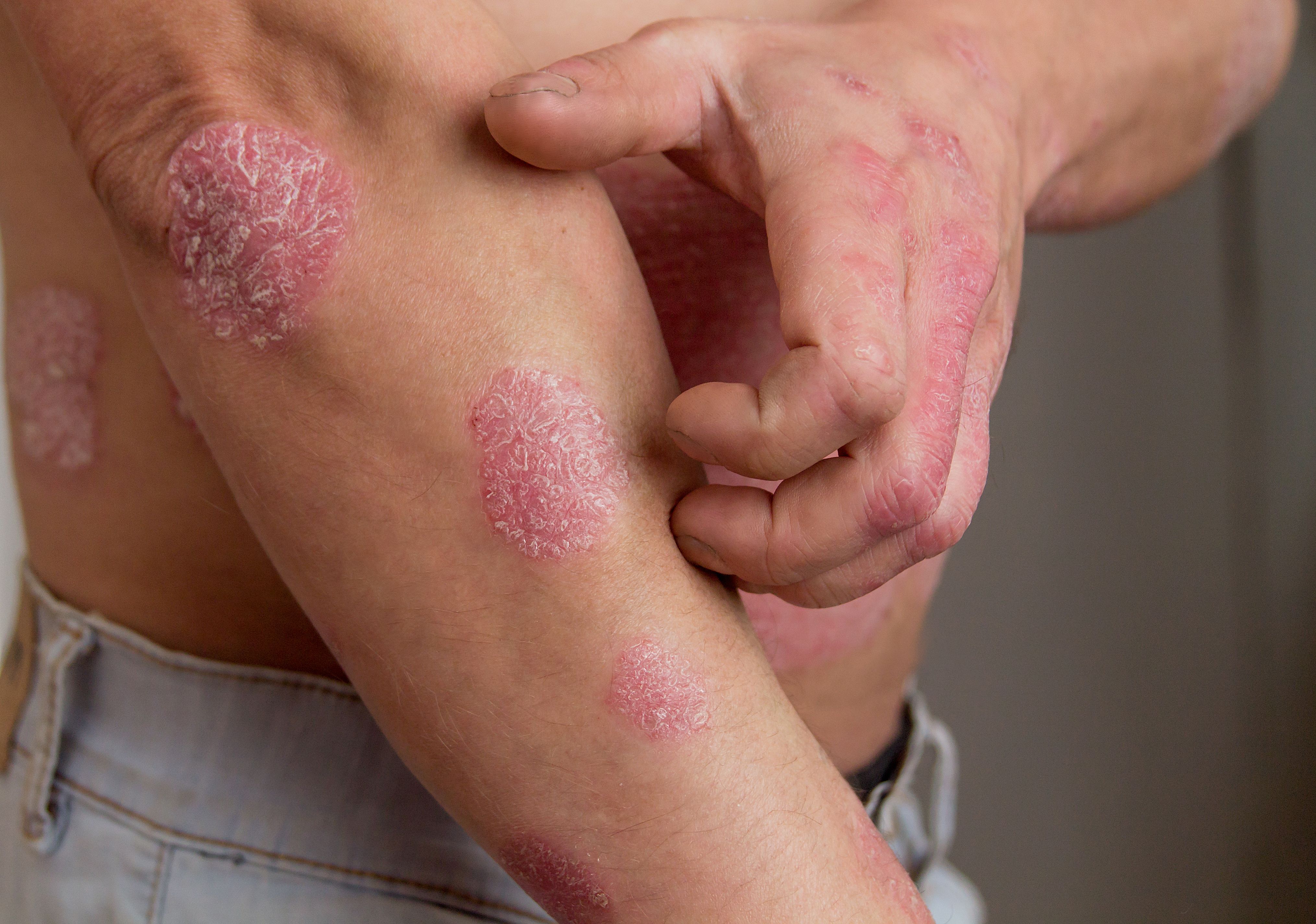
Emerging Therapies Plaque Psoriasis
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

The New England Journal of Medicine has published the clinical trial data from the PSOARING 1 and PSOARING 2 studies on tapinarof treatment for plaque psoriasis.

In a video for Dermatology Times®, Mark Lebwohl, MD, details how to match patients with the right psoriasis treatment for their specific needs.
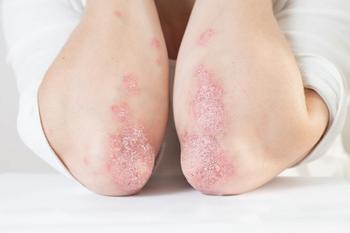
The pro-inflammatory transcription factor is critical for the expression of IL-23, which is known to play a role in psoriasis.
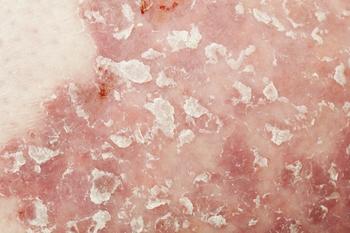
Voltaire-X study data shows that switching several times between Cyltezo and Humira results in similar pharmacokinetics, efficacy, immunogenicity, and safety in people with moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis.

A study found psoriasis patients treated with biologic therapy had a significant reduction in high-risk plaque in heart arteries over 1 year.
A new study in Arthritis Care & Research found depression and anxiety reduces the possibility of achieving minimal disease activity in patients with psoriatic arthritis.

New guidance statements related to COVID-19 vaccines and psoriatic disease patients have been published by the National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) COVID-19 Task Force.
Several systemic therapies are currently available for the treatment of patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis. Biologics changed the game for treatment. Continued study of and innovation in IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors promise even better results, but clinicians need to understand each biologic in detail.
A recent study found patients with high baseline cardiovascular risk who had taken ustekinumab were at increased risk for developing severe cardiovascular events following treatment.

Highlighting the relationship between long-term safety and drug survival, a recent review may help address physician reluctance in prescribing conventional systemic psoriasis treatments.

In a recent study, psoriasis drugs showed widely variable drug survival rates, owing to differences in safety, efficacy, patient satisfaction and other factors. However, concerns linger over potential to cause long-term cumulative organ toxicity.

Comorbidities, co-medication, organ impairment, functional deterioration and frailty make treatment plans challenging for older psoriasis patients. However, these patients should not be precluded but will require more extensive evaluation and assessment, according to a recent study.

A phase 3b study investigating the efficacy and safety of risankizumab compared to secukinumab showed positive results, with risankizumab demonstrating noninferiority to secukinumab at week 16, and superiority at week 52.

Phase 3 data show tildrakizumab’s (Ilumya, Sun Pharma) efficacy and safety last up to five years.

According to a recent meta-analysis, patients who stop and restart biologic treatment can regain psoriasis control without experiencing unexpected safety issues.

Using a novel autoantigen array, researchers have shown that the IgG4 anti-gliadin autoantibody might provide useful information for diagnosis and prognosis of psoriasis.

Twice-weekly treatment with calcipotriene-betamethasone diproprionate provides safe and effective maintenance treatment for plaque psoriasis, according to phase 3 data.

Studies offer further insight into risks associated with biologic therapy. One study suggests it’s not necessary to stop biologic therapy preoperatively to limit post-operative infections. Another systematic review does not rule out melanoma risk.

Phase 3 data announced at the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) Virtual Meeting Experience (VMX) 2020 demonstrate that the second-generation IL-17 inhibitor may offer long-lasting, safe treatment for patients with psoriasis.

With newer biologics consistently posting PASI improvements greater than 90%, dermatologists need to consider other factors when selecting a treatment. However, nuanced differences between the same drug class could be teased out, one expert says.

A recent study shows ixekizumab may be able to help treat moderate-to-severe cases of genital psoriasis.

A recent article shows oral apremilast may rapidly and significantly improve moderate-to-severe scalp psoriasis.


The latest set of guidelines for psoriasis being developed by the American Academy of Dermatology and the National Psoriasis Foundation will stress patient education and the need to align treatment strategies with patient lifestyles.

The latest American Academy of Dermatology-National Psoriasis Foundation phototherapy guidelines incorporate several advances in efficacy, safety and patient convenience that were unavailable a decade ago.