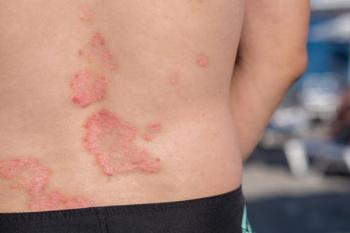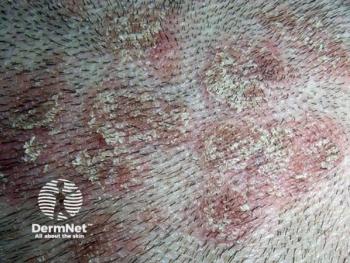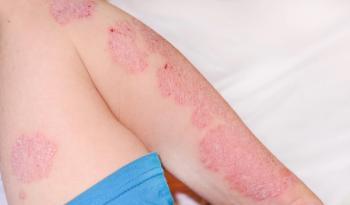
Considering comorbidities in psoriasis treatment
Treatment recommendations for psoriasis patients with specific comorbidities.
“Five years ago we only had the TNF blockers and ustekinumab, and ustekinumab wasn’t great for arthritis,” says Mark Lebwohl, M.D. He is the Waldman Professor and Chairman, Kimberly and Eric J. Waldman department of dermatology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. “But it was good in obesity. So, there was a very clear distinction regarding which drug we would use when. Now we have many more drugs, and a lot more to choose from.”
For PsA, expert opinion and recent guidelines from the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) and the National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) suggest TNF-alpha blockers or IL-17 blockers.1,2
“I believe that the best drugs for psoriasis are the ones that also inhibit radiographic progression in psoriatic arthritis,” says Alice Gottlieb, M.D., Ph.D. She is clinical professor, department of dermatology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, and medical director at Mount Sinai-Union Square in New York City. She co-authored the AAD-NPF guidelines.
PsA is the major comorbidity of psoriasis, she says, but many dermatologists do not even query their patients about it.
“We now have four TNF blockers and two IL-17 blockers that have FDA approval not only for moderate-to-severe psoriasis, but also for inhibition of radiographic progression, controlling signs and symptoms and improving quality of life in psoriatic arthritis. Thus, these drugs prevent progression of PsA in psoriasis patients who are being treated for their psoriasis but may be unaware they have psoriatic arthitis.”
PART OF THIS SERIES:
Disclosures:
Dr. Lebwohl is a paid consultant to Boehringer-Ingelheim. He is also an unpaid investigator for most other companies making biologics for psoriasis (Mount Sinai receives payment from these companies).
Dr. Gottlieb is a consultant and/or advisory board member for AbbVie, Allergan, Avotres Therapeutics, Beiersdorf, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Dermira, Eli Lilly, Incyte, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Novartis, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, Sun Pharmaceutical, UCB, Valeant (Ortho Dermatologics) and XBiotech. She has also received research/educational grants from Boehringer-Ingelheim, Incyte, Janssen, Novartis, XBiotech and UCB.
References:
1. Kaushik SB, Lebwohl MG. Psoriasis: which therapy for which patient. Psoriasis comorbidities and preferred systemic agents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:27-40.
2. Menter MA, Strober BE, Kaplan DH, et al. Joint AAD-NPF guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1029-1072.
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.