
Malignant melanoma can mimic many melanocytic lesions and vice versa, making it a difficult diagnosis. As such, accurate diagnosis should be a collaborative effort between clinician and dermatopathologist, says this expert.

Malignant melanoma can mimic many melanocytic lesions and vice versa, making it a difficult diagnosis. As such, accurate diagnosis should be a collaborative effort between clinician and dermatopathologist, says this expert.

There are many different aspects to the treatment and management of primary melanoma, but clinicians differ on their perceptions of the ideal treatment approach.

ASDS recently named Dr. Badia as the top national screener for the Choose Skin Health program, administering more then 1,800 screenings in the 2018-2019 program year.

For many years, genetic expression profiling has helped physicians predict which patients are at the highest risk of having their melanoma metastasize. Now, this same approach could aid in treating squamous cell carcinoma of the skin.

Radiodermatitis affects approximately 95% of all patients who receive radiation therapy for cancer - many of who are women undergoing breast cancer treatment. A recent study has found that developing the condition has a significant and detrimental impact on breast cancer patients' overall quality-of-life.

As age is the strongest risk factor in NMSC, dermatologists can see an increase in this type of cancer in elderly patients, and treatment preferences vary.

Comparative diagnosis of actinic keratosis (AK) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) in situ is needed for accuracy in treatment plan.

Melanoma located on the head and neck are associated with a potentially worse prognosis relative to alternate anatomical sites and peripherally located melanoma compared to those centrally located.


In a recent analysis, researchers examined whether results from a lesion diagnostic assay remained accurate after 12 months. The findings could alter how dermatologists approach future melanoma diagnosis in clinic.
Researchers recently examined a non-invasive test that, if additional studies can confirm, may directly affect future patient care for patients at risk for non-melanoma skin cancer.

Joel Cohen, M.D., shares his response to recent findings regarding the safety of chemical sunscreen and discusses why patients should consider using physical sunscreens.

A new technology based on laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy has demonstrated accuracy in both sensitivity and specificity for discriminating skin cancers from benign lesions, one expert says.
Combined imaging modalities may help guide choice of treatment and prevent biopsy, according to one expert.
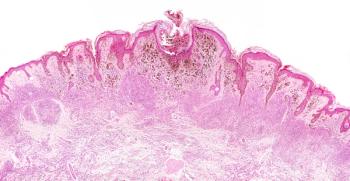
Accurately diagnosing some melanocytic neoplasms is challenging because they may fall into a grey area histologically, one expert says. Recent progress in molecular genetics can help dermatopathologists more precisely classify tumors, leading to more appropriate treatment and management choices.
GEP testing could improve staging accuracy and help streamline disease management, but more research is needed to determine if a high-risk GEP classification is associated with improved response to newer systemic therapies.
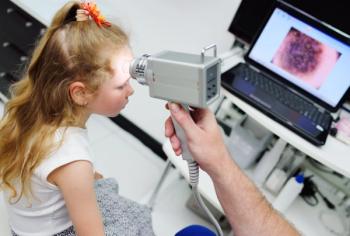
Read about the recent advancements in noninvasive imaging modalities that are making an impact on dermatological care.

Laser-assisted drug delivery used to fractionally ablate the target area prior to topical medical treatment can be useful in patients with widespread actinic damage, says this expert.

Dermatologists should work to gain a better understanding of immunologic pathways as well as the mechanisms of new and evolving immunotherapies, as these are key for understanding many current and emerging melanoma treatments, one expert says.

Sunscreen has been in the news as a recent study found that active ingredients in commercially available sunscreens quickly enter the bloodstream at levels far exceeding the recommended threshold. Still, researchers and physicians are urging Americans to continue using sunscreen, until more is known. These experts explain why.
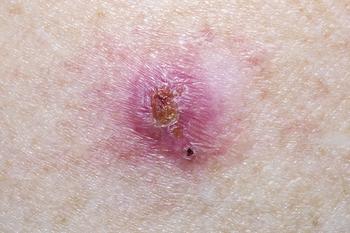
In this pipeline report, Dermatology Times presents insights into Hh pathway inhibitors currently in phase 2 and phase 3 for the treatment of basal cell carcinoma.
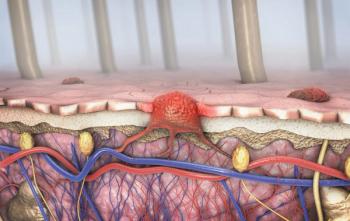
Innovative melanoma therapeutics are on the horizon. This pipeline report highlights some of the new drugs currently in phase 2, phase 3 or recently approved for the treatment of melanoma.
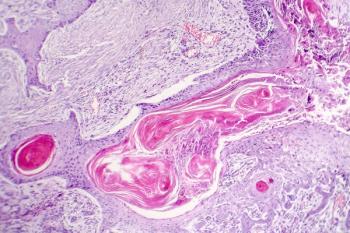
Better awareness in disease progression and improved understanding of field cancerization has shifted the thinking in management of patients with squamous cell carcinoma.
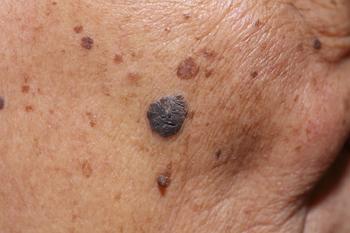
Learn about Nano-Pulse Stimulation and how this novel technology could potentially treat both benign and malignant dermatologic lesions.
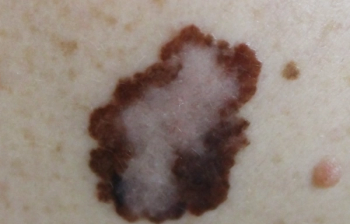
Sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) has classically been performed for regional disease control and to hopefully prevent disease metastasis; however, according to this expert, there has not been any good evidence to support this practice.