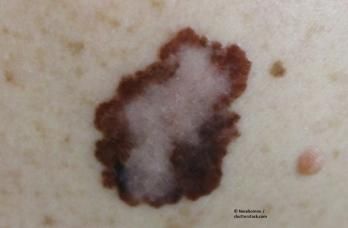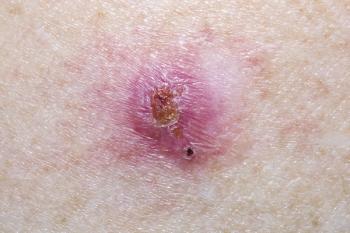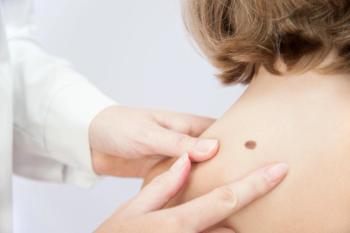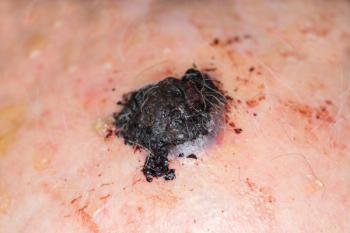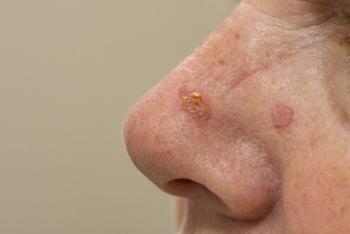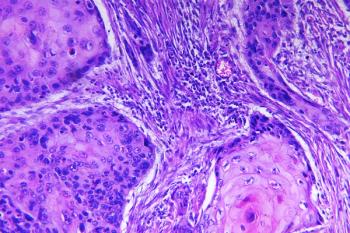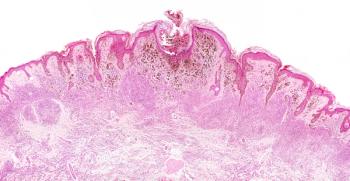
Patients may be afraid to use a sunscreen considering reports describing the potential for a variety of adverse effects. Physicians should seek a strong understanding of the evidence to discuss benefits and safety with patients and encourage proper sunscreen use.