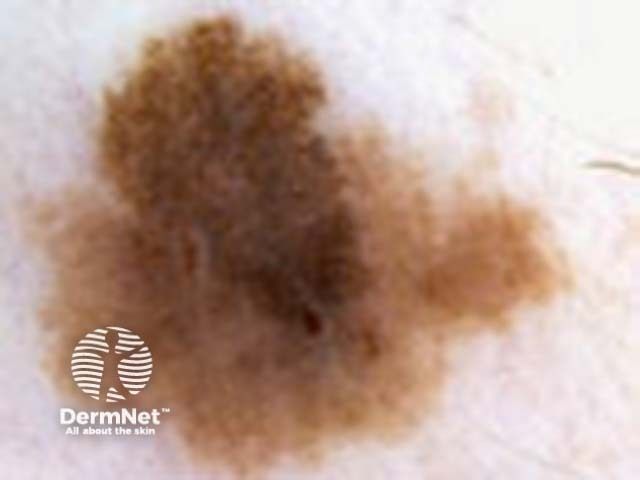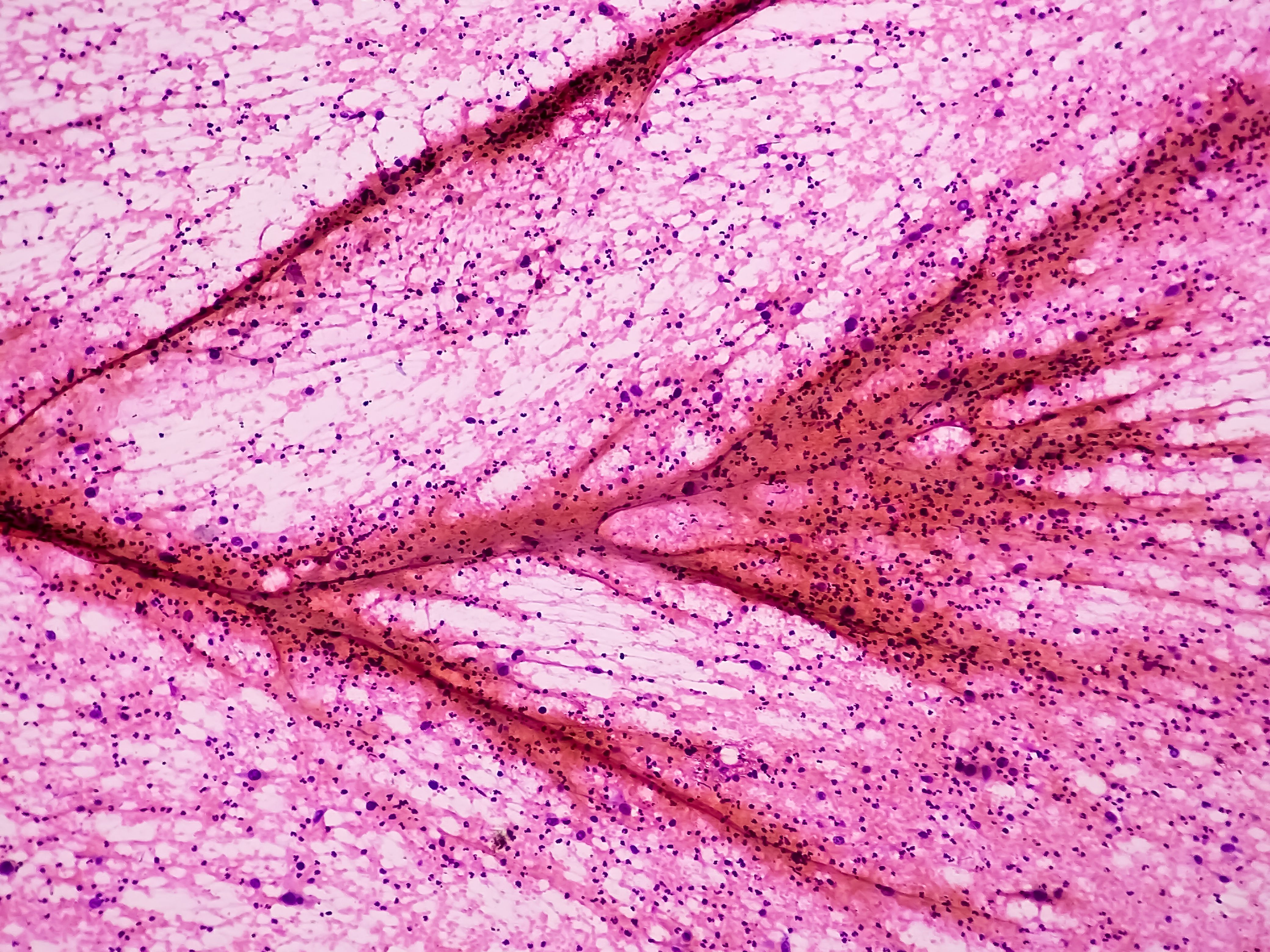
Skin Cancer
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

Discover 2024 skin cancer breakthroughs, including FDA approvals, innovative therapies, and updated clinical guidelines for melanoma and nonmelanoma care.

Despite the risks of sun exposure, a study found only a fraction of coaches receive adequate UV-related guidance from their associations or clubs.
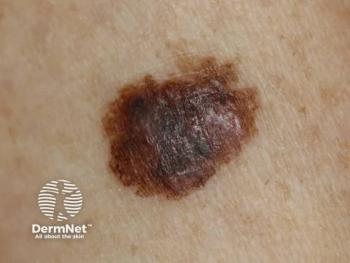
Researchers recommend limiting routine lipase tests to symptomatic patients or those with radiographic signs of pancreatic injury.

Certain factors may contribute to higher occurrences of non-melanoma skin cancer in these patients, according to a novel systemic review.

Pediatric melanoma, though rare, is the deadliest skin cancer in children, with 300-500 US cases annually.

Motivators like health benefits, altruism, and trust in clinicians enhance participant retention and adherence in melanoma research, according to MEL-SELF findings.

The study underscores the importance of addressing work-related concerns for patients with melanoma, advocating for effective communication about rehabilitation options.

Aaron Farberg, MD, explores advancements in melanoma and cSCC prognostic tools, the role of gene expression profiling in inflammatory diseases, and initiatives aimed at supporting early-career dermatologists at Fall Clinical 2024.

In October's cover feature, Nicole A. Negbenebor, MD, FAAD, discusses the benefits of intralesional 5-fluorouracil injection for older patients with squamous cell carcinoma who may elect to delay therapy or are not ideal candidates for surgery.

Farberg discusses data recently published in Geriatrics demonstrating low rates of recurrence.

Data was published in the Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine.
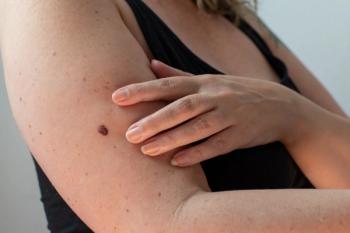
Swiss researchers found significant gender differences in melanoma care, including variations in information preferences and treatment decision-making.

The study, published in Dermato, showed that 92% of NMSC tumors showed measurable changes in depth of invasion from one image to the next.
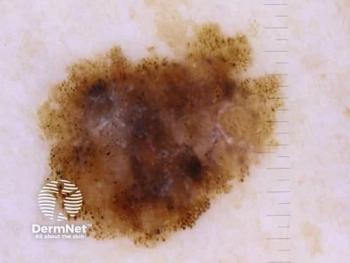
The PD-1/IL-2α bispecific antibody fusion protein is intended for patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic melanoma.

Earlier this summer, Meghan Heberton, MD, emphasized the importance and growth of the subspecialty.

Researchers tailored screening and surveillance schedules to individual risk of patients.
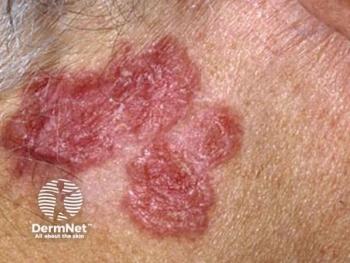
A comprehensive analysis of 71 studies revealed the highest lesion clearance and recurrence rates among individuals who had undergone surgery.

Despite high accuracy scores, the study found AI models often produce overly complex explanations, making them less effective for patient education.

The overall reduction of tumor size in all lesions treated in part 2 was approximately 86%.
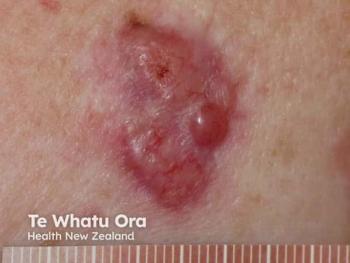
To improve overall outcomes for patients with large basal cell carcinomas, it has been beneficial to employ the use of vismodegib as a neoadjuvant and/or adjuvant treatment.

Researchers emphasized the need for improved reliability and regulatory frameworks for AI tools before they are integrated into dermatological practice.

Jacob Scott, MD, president and chairman of DaRT, shares highlights of the guidelines and what he hopes clinicians can glean from them.

In combination with cemiplimab, BNT111 contributed to statistically significant and improved overall response rates.

Researchers noted how historical bias in dermatology research has impacted the understanding and treatment of conditions in darker skin.

Margins < 1 mm also do not increase the risk of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma recurrence risk if the galea aponeurotica is not involved.