Atopic Dermatitis
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News


Significant variation exists in prescribing patterns among doctors managing atopic dermatitis, and the prescription of some drugs may go against dermatology guidelines, finds a recent study.

An expert speaks with Dermatology Times about the nuances of diagnosing, treating and managing eczema in black patients.

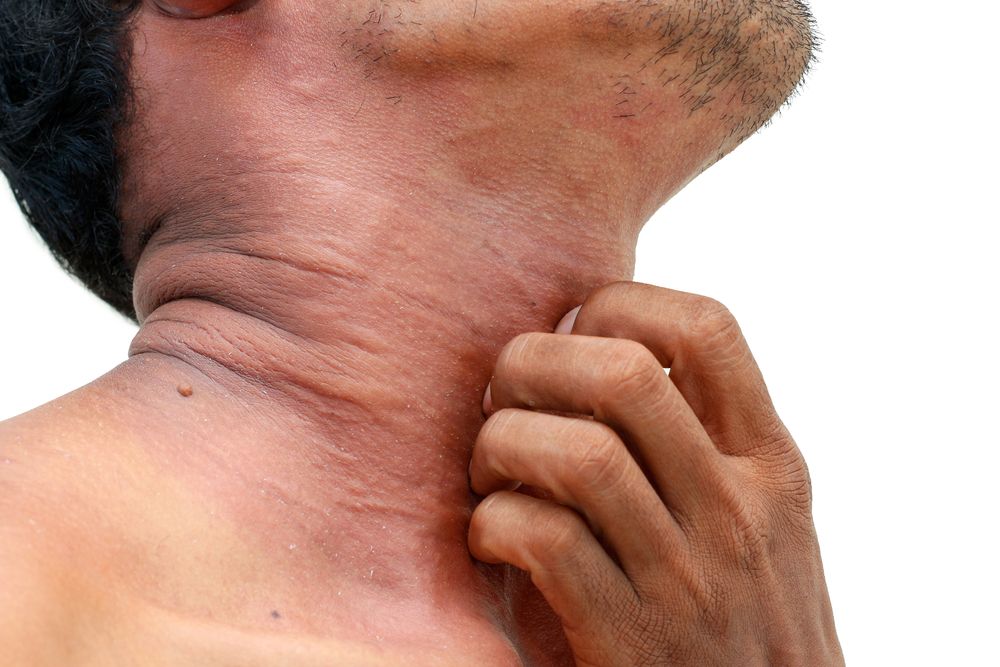
Children with atopic dermatitis - especially moderate-to-severe disease - seem to have an risk of developing other atopic diseases, such as asthma, allergic rhinitis and food allergies, says this expert.

Patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis may have a 20% increased risk of atrial fibrillation, finds a recent study.
For patients with atopic dermatitis, access to dermatology care appears to be best in the West and poorest in the Midwest, shows a recent study looking at disparities in access to services across the United States.
Understanding the pattern of pruritus in various autoimmune connective tissue diseases may help physicians identify different etiologies that will inform different treatment targets to alleviate the symptom, according to researchers who examined pruritus relative to disease.

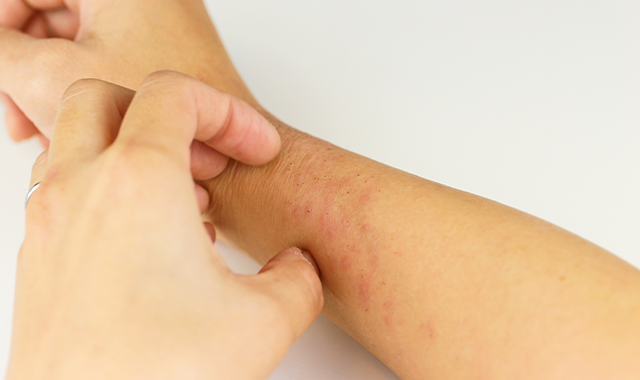
A recent study showing that patients perceive inflammation-associated itch as more intense and qualitatively different than itch without inflammation suggests that dermatologists target inflammation in conditions such as atopic dermatitis.

Not treating, incorrectly treating or undertreating eyelid eczema can result in significant patient suffering. Finding the root of the problem is key to safe and effective therapy, Dr. Peter Lio says.

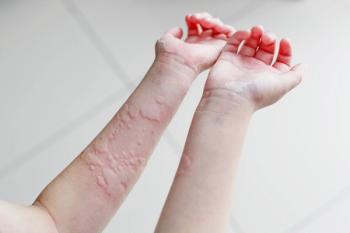
Lifestyle recommendations are an interesting and complex aspect of eczema care. There are many things that can impact eczema severity and are in a patient's control to a certain extent. However, offering suggestions that can actually help patients can be challenging, one expert says.

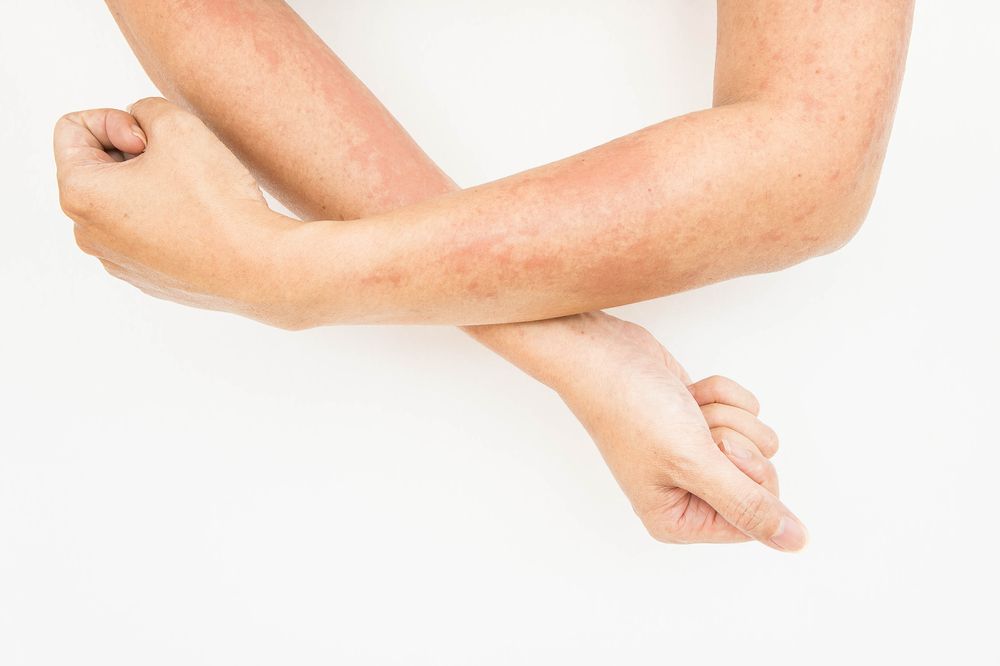
Adult atopic dermatitis patients with moderate-to-severe disease who were treated with systemic agents reported a high level of disease-related burden despite those treatments, says a recent study.

Bathing in a 0.5% apple cider vinegar solution isn’t a useful treatment for atopic dermatitis, and it can be irritating to the skin, report researchers in a recent study.

Stay up-to-date on the most recent clinical advances in atopic dermatitis.

In this interview, Dr. Anna De Benedetto discusses what initially drew her to dermatology and what inspired her to study atopic dermatitis in the elderly.

Adults 60 years and older tend to have a distinct atopic dermatitis presentation and important comorbidities, but dermatologists treating these patients find lacking evidence on how to diagnose and best treat atopic dermatitis in the elderly, according to a recent review.

A recent review provides a timely update regarding what is known about itch and skin barrier damage.

A recent study in experimental mice showed that interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 act as acute pruritogens, supporting the benefit of targeting these cytokines in the therapeutic planning of the patients with pruritus.

A study recently investigated the effects of probiotics on clinical symptoms, immune response, and gut microbiota in patients with atopic dermatitis. Dr. Lazzara explains what researchers discovered in this video.

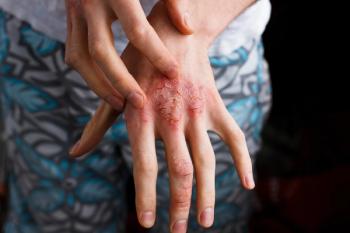
Real-world outcomes from treating adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis with dupilumab are similar to what researchers have found in clinical trials, according to this study.
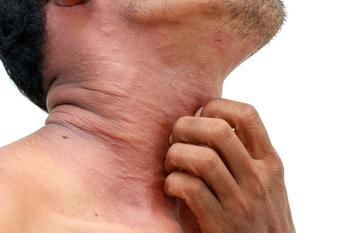
Pain is a distinct and important symptom of atopic dermatitis experienced by almost two thirds of patients, reports a recent study.

Researchers recently analyzed insurance claims data to investigate the safety and efficacy of off-label immunomodulatory drugs for atopic dermatitis in real life practice. Read what they discovered here.

Atopic dermatitis presents differently depending on whether the patient is an adult or child. This means that different treatments may be more effective in an adult than children and vice versa.
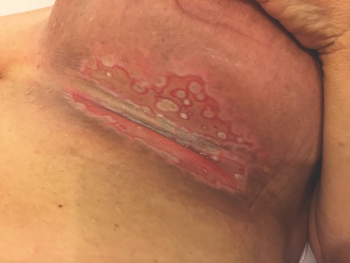
Dermatologists investigate better ways to treat radiodermatitis as it becomes increasingly common in breast cancer patients.