Atopic Dermatitis
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

Gladskin announces the launch of its over-the-counter eczema topical in the U.S, which features the company’s patented Micreobalance technology.
Adult patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis who were treated with systemic agents, including cyclosporine, azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, methotrexate or cyclophosphamide, reported a high level of disease-related burden despite those treatments, says a recent study.

Atopic dermatitis therapy is currently undergoing a revolution that promises to treat patients of all ages who are suffering from every aspect of the disease-from rashes, itch and sleep disturbances, to secondary effects, like anxiety and depression.

It’s an exciting time for atopic dermatitis patients as many new treatment options are on the market and in the pipeline. But treatment doesn’t yet offer a cure and many patients continue to suffer with symptoms, including itch, psychosocial and quality-of-life issues, according to a recent paper.

Abnormalities in epidermal barrier integrity, affecting factors such as epidermal calcium gradients, filaggrin, cornified envelopes, desquamation of corneodesmosomes and skin lipids, may also influence epidermal barrier dysfunction, according to a recent review.

A recent chart review found that eczematous eruptions occurred in 5.8% of patients using interleukin (IL)-17 inhibitors for psoriasis. Its authors believe that additional research could help identify which patients may be most at risk.
A phase 2 study shows that the oral Janus kinase (JAK) 1 inhibitor abrocitinib quickly improved atopic dermatitis (AD) severity and symptoms versus placebo with some measures achieving statistically significant separation in days.

Eli Lilly and Incyte announces positive results of two phase 3 clinical trials investigating the use of JAK inhibitor baricitinib as both a monotherapy and combination therapy for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis.
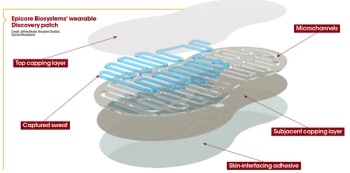
A wearable patch may soon be able to assess in flammatory biomarkers found in the sweat and interstitial fluid in individuals with atopic dermatitis to ultimately provide real-time information about their skin health.

The atopic dermatitis treatment dupilumab could offer a therapeutic option for keloids, according to a case report published in the Journal of European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.

Several new studies indicate that disease burden may be higher in adolescents than in adults with atopic dermatitis, and that adolescents with moderate-to-severe disease may face an even greater unmet therapeutic need.

The FDA announced it has accepted a priority review of dupilumab for the treatment of moderate-to-severe AD in pediatric patients 6 to 11 years of age. The drug is already approved for treatment of AD in adolescents and adults.

In a skit depicting Carnac the Magnificent, Drs. Rosen and Bhatia presented on 2020's new drugs and technologies at the current Maui Derm for Dermatologists, all with a magical twist.
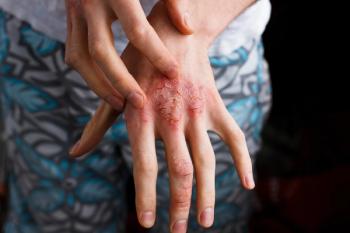
A recent study reports findings that support dupilumab as a safe, long-term treatment in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis.

With advancements in deep next-generation sequencing (NGS) and bioinformatics analysis, the authors of a recent study suggest the skin microbiome may hold promise as a clinical biomarker in atopic dermatitis (AD) management.
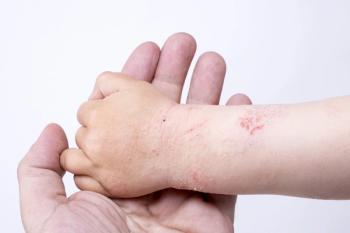
Anneke Andriessen, Ph.D. discusses research that suggests controlling symptoms with moisturizers can be an important - and inexpensive - prevention and treatment tactic for pediatric patients with atopic dermatitis.


Lifestyle recommendations are a complex aspect of eczema care. There are many things within in a patient's control that can impact severity and dermatologists should try to help patients identify these, one expert says.

A novel cocktail of topically applied botanicals has recently proven useful in the treatment and management of mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis in children, offering hope for this patient population.

Jeffrey Sugarman, M.D., Ph.D. provides his insight on the most significant changes in pediatric eczema treatment over the last few years.

LEO Pharma has recently announced that all three phase 3 studies examining the safety and efficacy of the atopic dermatitis investigational drug tralokinumab met all of its primary and secondary endpoints, leading way to the company now seeking marketing authorization for the drug.
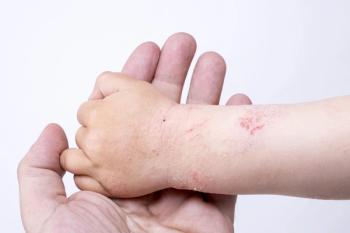
Biopsies are the gold standard approach for obtaining skin samples to test for biomarkers in atopic dermatitis, but tape strips may offer a far less invasive alternative for young children with the disease, research suggests.

Dermatologists should look for signs of conjunctivitis in their atopic dermatitis patients and learn how to manage the condition because this patients population may have an increased risk of experiencing conjunctivitis, particularly allergic conjunctivitis, according to a recent study.

Atopic dermatitis can have a profound impact on the quality of life of adolescents with skin of color. A recent review discusses special considerations for this patient population.
The U.S. FDA has granted Dermira with a Fast Track designation for its atopic dermatitis drug lebrikizumab following the start of phase 3 clinical trials to examine the efficacy, tolerability and safety of the drug.