
The study design emphasizes elevated endpoints, particularly joint health, ensuring that the most relevant outcomes are prioritized for patient care.
Maddi Hebebrand is an associate editor of Dermatology Times and joined the MJH Life Sciences team in May 2024. She attended Baldwin Wallace University, studying Media Production and Film, and received her Masters in Digital Media from Ohio University. When she's not writing, Maddi loves to read, attend concerts and spend time with her family.

The study design emphasizes elevated endpoints, particularly joint health, ensuring that the most relevant outcomes are prioritized for patient care.
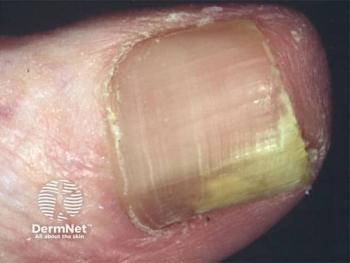
Efinaconazole demonstrated enhanced efficacy in treating nail fungal infections, thanks to its high penetration capability and low keratin binding.
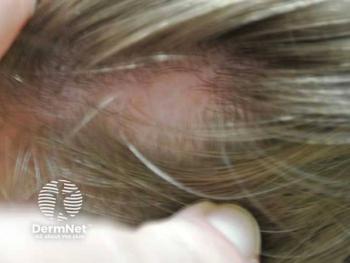
Researchers behind the trial saw a decrease in the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) score from 31 to 11.2 after 3 months of treatment with brevilin-A.

Researchers behind the study emphasized the urgent need to enhance the diagnostic skills of primary care practitioners to improve early detection of psoriasis.
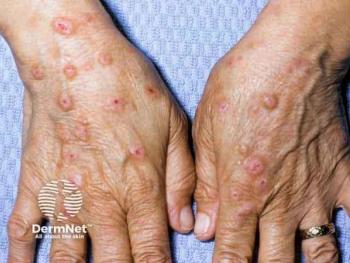
Significant reductions in itch scores and improved assessments of PN severity and quality of life were observed throughout the study.
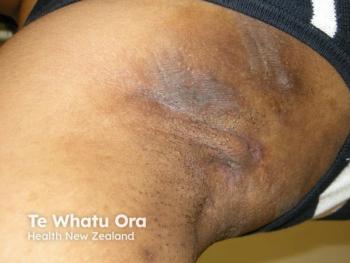
A recent review found clinical trials for HS lack diversity, limiting understanding of treatment efficacy for SOC populations.

Mease, the lead investigator on the trial, spoke about comparing varying mechanisms of action, primary and secondary endpoints, and how the results of BE BOLD could affect treatment choices.

Experts shared pearls for acne and rosacea care at Maui Derm NP+PA Fall.
A recent review found hair loss can severely impact self-esteem and body image, leading to social anxiety and emotional distress among affected youth.

In a Dermatology Times Case-Based Roundtable event, Andrew Alexis, MD, MPH, FAAD, reviewed 3 cases of patients with vitiligo treated with ruxolitinib cream.

Melinda Gooderham, MSc, MD, FRCPC, emphasized the significance of the study’s results, showcasing stable laboratory parameters over a 12-week trial.

A poster presented at the EADV Congress revealed the drug's long-term efficacy in treating AD, particularly in the head and neck regions.
The expanded dosage aims to provide healthcare providers with greater flexibility in treating larger or multiple areas affected by AK.
While researchers found both therapies effective in long-term use, they stated secukinumab showed quicker improvements in QoL.

Hypothyroidism and Hashimoto's thyroiditis were found to significantly increase the risk of developing AA, unlike hyperthyroidism.

A recent study indicated that 43.3% of lesions achieved a high efficacy score following Alexandrite laser therapy.

Researchers behind the review suggested that future research should prioritize large-scale trials to confirm abrocitinib's long-term safety and efficacy in various skin disorders.

This marks the first head-to-head trial of an IL-17A/F inhibitor against an IL-23 inhibitor in psoriatic arthritis treatment.

The company plans to release full 52-week OLE data for ESK-001 in early 2025, building on positive interim results.

After releasing promising data from several clinical trials, Burnett discussed the importance of studying efficacy and safety across diverse populations.
Nearly 44.2% of patients achieved HiSCR100, indicating a complete resolution of HS symptoms by the end of the 2-year period.

Key highlights of the presentations included data on delgocitinib for atopic hand eczema, and tralokinumab for head and neck atopic dermatitis.

“It is critical that our clinical data represent the diversity in the world around us, and these results further reinforce our commitment to providing meaningful innovation for immune-mediated skin diseases," said Patrick Burnett, MD, PhD, FAAD, chief medical officer of Arcutis.
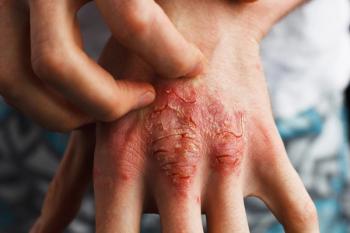
The findings stem from post-hoc analyses of previous trials, which found that 75.1% of patients reached PASI100 after 1 year on bimekizumab.

Through collaboration with Nimbus Therapeutics and Schrodinger, zasocitinib�’s AI-driven design maximizes its fit within the targeted enzyme.

Mona Shahriari, MD, FAAD, shared insights into prevalence, clinical presentations, increasing research diversity, and advocating for representation.
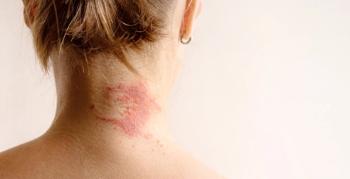
The study found that over 80% of patients who responded to lebrikizumab at week 16 maintained clear or almost-clear skin after 3 years.
Christopher Bunick, MD, PhD, shared insights into zasocitinib’s presented data and ongoing clinical trials.

Learn more about the latest in dermatology from Sheila Fallon Friedlander, MD; Melodie Young, MSN, ANP-c; Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, MSCI; Julie Harper, MD; and Matthew Zirwas, MD.

Announcements from both the FDA and the EC were supported by 2 clinical trials that evaluated the safety and efficacy of delgocitinib cream.