Patient Selection for Potential OX40-OX40L–Based Treatment Strategies
Panelists discuss how OX40 pathway–targeted therapies may benefit specific patient subsets with particular immunologic profiles and could potentially modify the disease course when used early, although patient selection criteria remain unclear.
Episodes in this series

Video content above is prompted by the following:
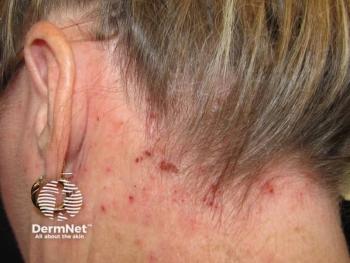
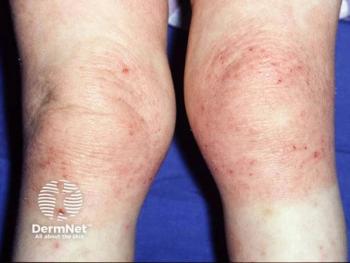
Current clinical programs suggest OX40-OX40L therapies may not provide universal one-size-fits-all solutions but could identify specific patient subsets who achieve remarkable long-term responses. Dr Eichenfield draws parallels with allergic contact dermatitis patterns, where some patients achieve significant improvement through trigger avoidance while others show minimal response despite environmental modifications. This heterogeneity in antigen-driven immune responses reflects the complex immunologic history and development that varies among individuals, suggesting that personalized approaches may be necessary for optimal therapeutic outcomes.
The experts discuss how immunologic responses evolve throughout a patient’s life, from early childhood through adulthood, creating different therapeutic targets at various disease stages. Using an analogy of “bullies” representing effector cells, targeting OX40 ligand may prevent the development of inflammatory cells (preventing bullies from forming), while OX40 targeting may reduce existing effector cell numbers and effectiveness (addressing existing bullies). This developmental perspective suggests that early intervention with OX40-OX40L therapies might modify long-term disease trajectories and reduce flare frequency over time.
Clinical program data reveal some patients achieving seemingly incredible long-term responses, with sustained clearance periods extending well beyond active treatment. Although the mechanisms behind these durable responses remain unclear––whether representing true disease modification, on-drug effects, or induced remission––the potential for prolonged therapeutic benefits could transform treatment paradigms. This shifts the therapeutic conversation from disease control and impact minimization toward the possibility of disease cure or extended remission, addressing fundamental patient desires for lasting therapeutic solutions rather than lifelong management strategies.
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.