Overview of Emerging OX40 Pathway–Targeted Therapies in Development for Atopic Dermatitis
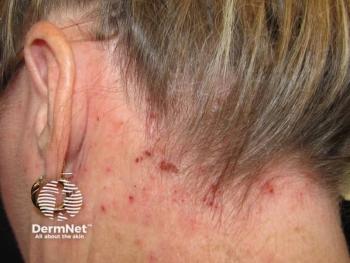
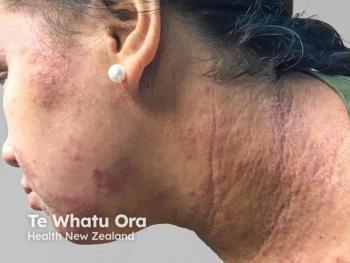
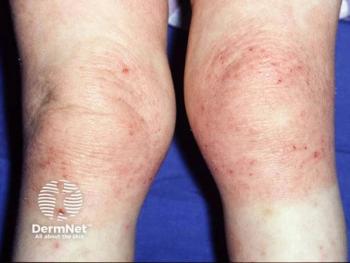
Panelists discuss how multiple OX40 pathway–targeted drugs are in development, including rocatinlimab (anti-OX40, cell depleting) and amlitelimab (anti-OX40L, nondepleting), both showing promising phase 2/3 results with potential for sustained responses.
Episodes in this series

Video content above is prompted by the following:
The OX40 pathway therapeutic landscape features 2 advanced candidates in phase 3 development: rocatinlimab, an anti-OX40 monoclonal antibody optimized for T-cell depletion, and amlitelimab, an anti-OX40 ligand monoclonal antibody designed as a nondepleting agent targeting antigen-presenting cells. Additional therapies in earlier development include IMG-007 (anti-OX40, phase 2), STAR-0310 (half-life extended anti-OX40, nondepleting), and APG990 (extended anti-OX40 ligand being studied in combination with IL-13 targeting), representing diverse mechanistic approaches within the pathway.
The therapeutic approaches differ fundamentally in their cellular targets and depletion characteristics. Amlitelimab blocks OX40 ligand on antigen-presenting cells without cell depletion, potentially impacting the “development of inflammatory cells,” whereas rocatinlimab targets OX40 receptors on T cells with cell-depleting properties, “decreasing the number of existing inflammatory cells.” These mechanistic differences may translate to distinct clinical profiles, safety considerations, and patient-specific therapeutic advantages, though comparative clinical data remain limited given the heterogeneous patient populations and different study designs.
Both leading candidates have demonstrated primary end point achievement in their respective clinical programs, with rocatinlimab showing positive results across multiple phase 3 studies (ROCKET HORIZON, ROCKET IGNITE) and amlitelimab meeting primary end points in the phase 2B STREAM-AD study, with phase 3 readouts pending. The extensive clinical development programs will provide crucial data on comparative efficacy, safety profiles, and optimal patient selection strategies. The success of these programs will determine how OX40-pathway therapies integrate into the existing therapeutic landscape and potentially establish new treatment paradigms for atopic dermatitis management.
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.