Enhancing Biologic Use in Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Key Takeaways
- Biologics are increasingly favored for HS management, with bimekizumab showing strong efficacy and patient-reported benefits.
- Bimekizumab's dual IL-17A/IL-17F inhibition offers significant improvements in HS, with sustained efficacy over 96 weeks.
At a Dermatology Times Case-Based Roundtable event, Joe Gorelick, MSN, FNP-C, reviewed real-world strategies for hidradenitis suppurativa, highlighting growing preference for bimekizumab based on its dual IL-17A/IL-17F inhibition.
“HS is one of those conditions that when it happens, it will derail your entire day, and rightfully so. Sometimes you have to stop and give these patients the attention they need,” said Joe Gorelick, MSN, FNP-C, during a recent Dermatology Times Case-Based Roundtable event in San Francisco, California.
Gorelick, a certified family nurse practitioner at Schweiger Dermatology Group in San Jose, moderated a roundtable discussion centered on the best use of biologics when treating patients with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS).
Case #1
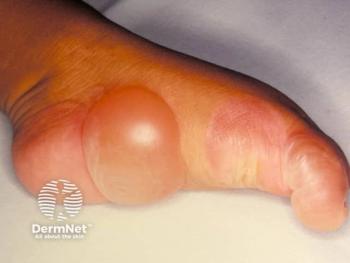
A 27-year-old woman with a 3-year history of HS presents with recurrent axillary nodules that significantly impair daily functioning. Examination reveals a single inflammatory nodule with established rope-like scarring in the left axilla, consistent with progressive, chronic disease. Despite sequential use of topical clindamycin, oral doxycycline, combination oral clindamycin/rifampin, metformin, and hormonal therapy, she has experienced inadequate control and persistent symptomatic burden.
Pain, drainage, and concern about further scarring have contributed to increasing psychosocial distress, highlighting the need for escalated intervention. Given her refractory course and functional limitations, Gorelick noted that initiation of biologic therapy is appropriate to target the underlying inflammatory pathways and reduce future lesion formation.
Gorelick reviewed with attendees data on secukinumab (Cosentyx; Novartis), bimekizumab (Bimzlex; UCB), and adalimumab (Humira; AbbVie). In the SUNSHINE trial (
In the BE HEARD I (
“I ended up in an HS Reddit forum, which I felt is helpful for understanding the patient experience. Half of the Reddit thread was about bimekizumab and people talking about their life-changing experiences after trying different medications,” said one attendee.
The attendees emphasized bimekizumab’s dual IL-17A/IL-17F inhibition and higher HS-specific dosing, highlighting the strong delta versus placebo in the BE HEARD 1 & 2 trials. The program also reviewed long-term extension results showing sustained improvement through 96 weeks, including notable HiSCR 100 rates, described as an “incredibly high bar” for HS response
In the PIONEER I (
Case #2
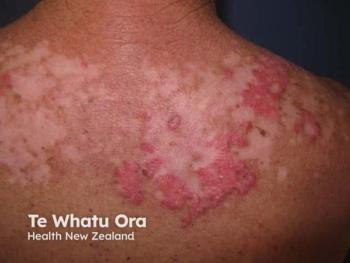
A 35-year-old man with a 6-year history of moderate HS presents with recurrent axillary and groin nodules and abscesses that flare approximately monthly. His disease has led to persistent pain, drainage, and functional limitations, affecting both occupational performance and intimacy. Despite treatment with topical clindamycin, intermittent oral antibiotics, and episodic corticosteroids for flares, symptom control remains inadequate.
His decision to decline biologic therapy 2 years prior was based on concerns about treatment duration and potential adverse effects; however, increasing frustration with ongoing disease activity has prompted reevaluation of management options. Given his chronic, relapsing course and significant quality-of-life burden, escalating to a targeted biologic therapy is appropriate to address the underlying inflammatory pathways, reduce flare frequency, and prevent further tissue damage.
With the second case, Gorelick reviewed long-term efficacy data for secukinumab and bimekizumab. For patients who responded well to the initial 4-week secukinumab dosing and continued, 69.8% achieved HiSCR75 and 47.9% achieved HiSCR90 at week 104. For bimekizumab, 85.4% of patients maintained HiSCR50 at 96 weeks, 77.1% maintained HiSCR75 at 96 weeks, and 57.6% maintained HiSCR90 at 96 weeks.
The group agreed that bimekizumab is increasingly becoming a first-line biologic choice for patients with significant inflammatory burden, monthly flares, or impaired quality of life. The candidal infection risk (approximately 10% in trials) was acknowledged but viewed as manageable: “Would that prevent you from prescribing it?… We can handle a thrush,” Gorelick said.
Practice Takeaways
The Case-Based Roundtable event centered on real-world management of moderate to severe HS and highlighted the growing role of biologics, particularly bimekizumab, as clinicians shift away from older systemic approaches toward targeted inflammatory pathway control. The attendees repeatedly discussed HS as “one of the most horrific conditions we have in dermatology” and emphasized early recognition, proactive intervention, and aggressive multimodal treatment strategies.
Bimekizumab was described as more impactful, both in trial data and patient-reported experience when compared with secukinumab and adalimumab. Overall, the event positioned bimekizumab as a highly effective, well-tolerated option with strong clinical efficacy, while secukinumab remains a viable alternative with long-term safety and dose-flexibility data. Adalimumab, though foundational, was portrayed as less aligned with current expectations for HS disease control.
Find an upcoming Case-Based Roundtable event near you,
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.