- Dermatology Times, December 2019 (Vol. 40, No. 12)
- Volume 40
- Issue 12
Pruritus characteristics in psoriasis
Pruritus frequently afflicts psoriasis patients, but few studies explore the role of pruritus in regards to disease activity, pharmacotherapy or demographics. This study attempts to fill that gap.
A study published in Advances in Dermatology and Venereology in April of 2019 focused on pruritus in psoriasis. The study was led by Jacek Szepietowski, M.D., from the Department of Dermatology in Wroclaw Medical University, Poland. The aim of the study was to describe the prevalence of pruritus in psoriasis as well as to detail the clinical characteristics.
A cross-sectional study was performed. 143 patients (83 males and 60 females) with psoriasis vulgaris were included in the study. The subjects included provided a detailed history, laboratory tests, and physical exams were completed that included PASI, BSA and physician's global assessment.
The study showed that the prevalence of pruritus is psoriasis is 72%. Chronic pruritus was present in both young patients and older patients with psoriasis. Patients with pruritus had high rates of xerosis. In this patient cohort the mean values for PASI was 14.6 ± 9.5 points. The mean value for BSA was 27% ± 21%. The mean value for PGA was 2.1 ± 1.0 points.
There was a correlation between systemic comorbidities and pruritus, specifically anemia was associated with higher itch intensity. Another comorbidity that was associated with increased pruritus was diabetes. Interestingly, aspirin use was also more common in patients with pruritus.
Several variables were negatively associated with pruritus in psoriasis. For instance emollients were associated with decreased chronic itching. Several comorbid conditions and medications also were negatively associated with pruritus in psoriasis such as the presence of hypertension as well as treatment with psychiatric drugs and allopurinol.
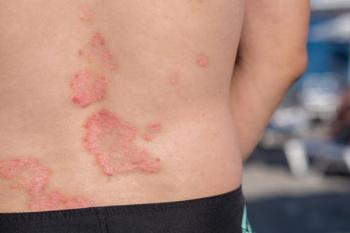
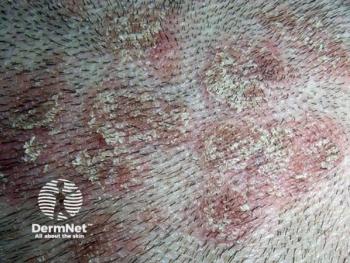
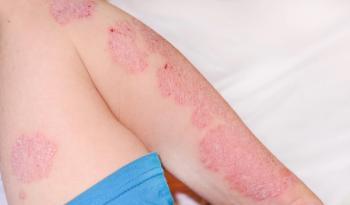
Pruritus was reported mainly in the lower limbs, back, and upper limbs with 66%, 49.5% and 47.6% of the patients reporting chronic itch in these areas, respectively. The vast majority of the subjects (77.7%) complained of pruritus in the pathologically changed skin.
The take home message for dermatologists based on the results of this study are the following:
- The majority of patients with psoriasis vulgaris suffer from chronic pruritus.
- Effective treatment for psoriasis will improve the pruritus in the majority of patients.
- There are other factors such as comorbid conditions and medication that may also contribute to pruritus and should be considered (i.e. diabetes).
The findings of this cross-sectional study suggest that pruritus is a salient feature present in the majority of psoriasis patients. It appears that several comorbid conditions as well as pharmacotherapies contribute to chronic itch both by modulating psoriasis and through independent mechanisms. More research is needed to better understand psoriasis associated pruritus and its relationship with comorbid conditions.
References:
Reszke, Radomir, RafaÅ BiaÅynicki-Birula, and Jacek C. Szepietowski. "Itch in psoriasis: a new look at well-known subject." Acta dermato-venereologica 99.3 (2019): 429-434.
Articles in this issue
about 6 years ago
Diet may impact squamous cell carcinoma riskabout 6 years ago
Genetic expression testing still a work in progress for melanomaabout 6 years ago
New resource for teens with atopic dermatitisabout 6 years ago
When is the right time to retire?about 6 years ago
40 years of champions in dermatologyabout 6 years ago
A novel target for rosacea treatmentabout 6 years ago
Should dermatologists embrace AI?about 6 years ago
Spironolactone efficacy may be similar to oral antibiotic TxNewsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.