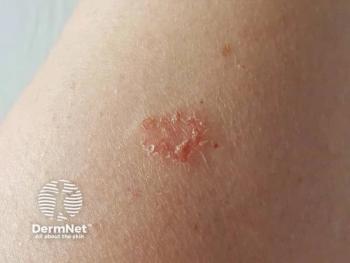
Sun Pharma’s Cosibelimab-ipdl (UNLOXCYT) Enters US Market for Advanced CSCC
Key Takeaways
- Cosibelimab-ipdl is a novel anti–PD-L1 antibody with a dual mechanism, engaging both adaptive and innate immune systems for tumor killing.
- The therapy is indicated for advanced CSCC patients unsuitable for surgery or radiation, offering a new systemic immunotherapy option.
Sun Pharma has launched cosibelimab-ipdl for advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, offering new hope for patients with limited treatment options.
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries has announced the US availability of cosibelimab-ipdl (UNLOXCYT), a novel anti–PD-L1 monoclonal antibody, for the treatment of adults with advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (aCSCC).1 The therapy is indicated for patients with either metastatic CSCC (mCSCC) or locally advanced CSCC (laCSCC) who are not candidates for curative surgery or radiation, a population with historically limited therapeutic options and high morbidity.
A Novel Dual Mechanism of Action
Cosibelimab-ipdl is administered as a 1,200-mg intravenous infusion over 60 minutes every 3 weeks. It is now available through a limited distribution network of authorized specialty distributors and one contracted specialty pharmacy. To facilitate access and adherence, Sun Pharma has launched UNLOXCYT SUPPORT, a comprehensive program designed to provide resources for healthcare professionals and patients, including assistance with access, affordability, and treatment navigation.
"UNLOXCYT is an evolution in checkpoint inhibition, combining durable efficacy with a proven tolerability profile for a group of aCSCC patients who traditionally would struggle to strike that therapeutic balance," said Richard Ascroft, CEO of Sun Pharma North America. "Sun Pharma is committed to ensuring access from day one with the UNLOXCYT SUPPORT patient access and affordability program."1
Unlike conventional PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitors, cosibelimab-ipdl is an anti–PD-L1 antibody that is capable of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). In vitro data suggest that this allows the drug to engage not only the adaptive immune system through checkpoint blockade but also the innate immune system via effector cell–mediated tumor killing, while preserving PD-L2 signaling. Although this multifaceted mechanism is based on preclinical in vitro findings and may not fully translate into clinical outcomes, it provides a biologic rationale for the balanced efficacy and tolerability profile observed in trials.
Pivotal Trial Data and Label Updates
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved an updated label for cosibelimab-ipdl that incorporates long-term follow-up data from the pivotal CK-301-101 clinical trial.2 The data demonstrated improvements in objective response rates, including a higher proportion of complete responses, as well as sustained durability of response over time. Importantly, the updated label did not reveal any new safety signals, confirming that the favorable tolerability profile seen in earlier analyses has been maintained with extended follow-up.
In the study, at least 50% of treated patients achieved an objective response, defined as a complete or partial response, across both metastatic and locally advanced disease cohorts. Complete responses were observed in 13% of patients with mCSCC and in 26% of those with laCSCC. When stable disease was included, the disease control rate reached 71%, reflecting a substantial proportion of patients deriving benefit from therapy. Notably, the median duration of response had not yet been reached in either group at the time of the analysis.
Safety and Tolerability Profile
Cosibelimab-ipdl demonstrated a strong safety profile consistent with immune checkpoint inhibition but with a low rate of severe immune-mediated adverse reactions. The most common adverse reactions were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, rash, diarrhea, and hypothyroidism. Immune-mediated adverse reactions were predominantly Grade 1 or 2. Only 0.9% were Grade 3 and limited to dermatologic events, with no Grade 4 or higher immune-mediated toxicities reported. None of the patients developed Grade 3 or 4 pneumonitis, a potentially serious complication of checkpoint inhibitors. Only 2 patients (0.9%) experienced pneumonitis, and both cases were Grade 2.
Addressing an Unmet Need in aCSCC
CSCC is one of the most common malignancies of the skin, yet a clinically meaningful subset of patients—estimated at roughly 40,000 annually in the US—progress to advanced disease, leading to approximately 15,000 deaths each year. Tumors frequently arise in cosmetically and functionally sensitive areas of the head and neck and may invade nerves, blood vessels, and adjacent structures, making surgery and radiation difficult or impossible. With this launch, cosibelimab-ipdl becomes a new systemic immunotherapy option specifically positioned for older, medically complex patients who often characterize advanced CSCC in real-world practice.
"Patients with unresectable or metastatic CSCC now have a new and important treatment option to manage their disease. UNLOXCYT is a novel anti–PD-L1 antibody that is capable of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and associated with clinically meaningful efficacy, as shown by a disease control rate of 71%," said Ann W. Silk, MD, MS, medical oncologist at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Assistant Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School. "Because these patients tend to be older and have multiple comorbidities, it's extremely valuable to have a therapy that offers durable disease control and proven tolerability."1
References
1. Sun Pharma Announces the Availability of UNLOXCYT™ (cosibelimab-ipdl) for Advanced Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma (aCSCC). News release. PR Newswire. Published January 15, 2026. Accessed January 16, 2026.
2. Ruiz ES, Muñoz-Couselo E, Montaudié H, et al. Efficacy and safety of cosibelimab in advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: Results from a Pivotal Open-label Study with a median follow-up of ≥2 years. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2026;94(1):48-56. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2025.09.009
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.
.png)