Journal Digest: September 10, 2025
Key Takeaways
- Fused 3D models of tongue squamous cell carcinoma enhance visualization of tumor orientation and margins, aiding surgical planning and discussions.
- Persistent nodules from hyaluronic acid fillers require higher hyaluronidase concentrations for effective treatment, underscoring the need for standardized protocols.
This review of the latest dermatologic studies highlights new research on novel image fusion for tongue SCC, persistent nodules following HA fillers, rice bran extract for wound healing, and more.
Journal of the Sciences and Specialties of the Head and Neck |
This study evaluated the feasibility of creating fused 3D models of oral squamous cell carcinoma using both preoperative MRI and postoperative histopathology in 9 tongue cancer cases. The researchers used a 3D table scanner and modeling software to reconstruct the tumor within resected specimens, aligning anatomical landmarks to accurately superimpose MRI and histological data. Results showed that MRI-based models generally overestimated tumor size compared to histopathology, likely due to imaging artifacts, inflammation, and tissue shrinkage. Despite these discrepancies, the fused 3D models improved visualization of tumor orientation and margins, offering potential benefits for surgical planning and multidisciplinary discussions. The method proved applicable for both partial and total glossectomy specimens without altering standard pathology workflows. Future developments could include AI-assisted automation to enhance model accuracy and efficiency.1
Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology |
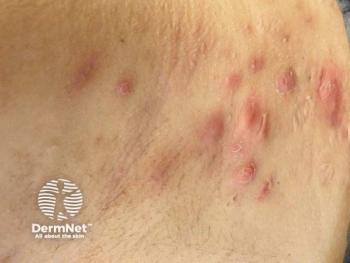
This case report describes a rare complication following hyaluronic acid (HA) "skinbooster" filler injections for necklines. A 40-year-old woman developed persistent, treatment-resistant non-inflammatory nodules in the neck after superficial HA injections. Despite 5 previous sessions of hyaluronidase at another clinic, no improvement was observed over 6 months. Upon presentation, the nodules were firm, non-tender, and located superficially. The treating physicians used a higher-than-standard concentration of hyaluronidase (300 IU/mL), resulting in significant improvement within one week and high patient satisfaction. Currently, no standardized protocol exists for managing persistent filler-related nodules, highlighting the need for further research. This is the first known report of such persistent neck nodules, contributing valuable insights to the aesthetic dermatology literature.2
Experimental Dermatology |
This study investigates the therapeutic effects of rice bran extract (RBE) in treating radiation dermatitis, a common and painful side effect of cancer radiotherapy. Radiation dermatitis affects up to 95% of patients and is driven by oxidative stress and chronic inflammation. Current treatments primarily manage symptoms without addressing underlying causes. RBE was found to be rich in antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds such as pyrogallol, gallic acid, and ferulic acid. In vitro, RBE reduced inflammatory marker IL-6, enhanced antioxidant activity, stimulated procollagen production, and promoted fibroblast migration—key factors in wound healing. In a mouse model, topical RBE significantly reduced skin damage, inflammation, ulceration, and fibrosis while enhancing epithelial regeneration. RNA sequencing showed RBE modulated pathways involved in inflammation resolution, skin repair, and metabolic regulation, with Pparg identified as a key regulatory gene.3
Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology |
This comprehensive review introduces "skinspan", a novel concept in aesthetic and regenerative medicine that parallels “healthspan”—defining the duration of skin’s youthful, healthy appearance. The authors propose skinspan as both a clinical framework and consultation tool to guide long-term skin health strategies. They review the molecular drivers of skin aging, including genomic instability, cellular senescence, mitochondrial dysfunction, and proteostasis decline, and examine evidence-based interventions across lifestyle, topical, systemic, and procedural domains. A tiered intervention algorithm is proposed. The review emphasizes synergistic, proactive strategies to extend skinspan and prevent premature aging. While current evidence supports many interventions, the authors call for more randomized controlled trials to validate and refine approaches.4
Lasers in Surgery and Medicine |
This study evaluated the safety and efficacy of the Symmed radiofrequency (RF) device for noninvasive body contouring and skin improvement in the abdomen/flanks. Fifteen adult participants underwent eight RF treatment sessions over several weeks. The researchers measured changes in body circumference, fat layer thickness, and dermal echogenicity (an indicator of collagen content) using ultrasound and photographs. Results showed a significant 2% reduction in body circumference, 9% decrease in subcutaneous fat thickness, and a 12% increase in skin echogenicity, indicating improved collagen structure. Photographic assessments confirmed visible improvements in body contour and skin appearance, with high accuracy in before/after identification by evaluators (84%). Participants reported high satisfaction, and no serious adverse effects occurred—only minor, temporary discomfort or redness.5
References
1. Koivuholma A, Sistonen HJ, Aro K, et al. Three-Dimensional Presentation of Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma Histopathology and Magnetic Resonance Imaging - A Novel Image Fusion Method. Head Neck. Published online September 4, 2025. doi:10.1002/hed.70032
2. AlBargawi S. Persistent Nodules on Necklines Following Hyaluronic Acid Filler: A Case Report. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025;24(9):e70442. doi:10.1111/jocd.70442
3. Kuan CH, Hideki T, Wu CH, et al. Rice Bran Extract Alleviates Inflammation and Promotes Wound Healing in Radiation Dermatitis. Exp Dermatol. 2025;34(9):e70162. doi:10.1111/exd.70162
4. Kream E, Fabi SG, Boen M. Skinspan: A Holistic Roadmap for Extending Skin Longevity With Evidence-Based Interventions. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025;24(9):e70432. doi:10.1111/jocd.70432
5. Santos AF, Fernández AI, Fernández LS, Zapico LH, Freitag SV. Body Shaping and Skin Appearance Improvement in the Abdomen and Flanks by Radiofrequency Technology. Lasers Surg Med. Published online September 4, 2025. doi:10.1002/lsm.70059
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.