- Dermatology Times, December 2025 (Vol. 46. No. 12)
- Volume 46
- Issue 12
Dual IL-17A and IL-36R Blockade Demonstrates Rapid Remission in Refractory Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Key Takeaways
- Dual inhibition of IL-17A and IL-36R targets 2 synergistic cytokine pathways central to hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) pathogenesis.
- A combination of secukinumab (anti–IL-17A) and recibokibart (anti–IL-36R) led to rapid and complete resolution of refractory Hurley stage III HS in this case.
Emerging biologic combinations may open a new therapeutic frontier for severe hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) that fails to respond to conventional and single-pathway biologics.
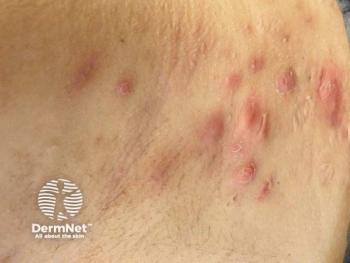
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) affects approximately 1% of the global population as a chronic inflammatory skin disorder with a profound impact on patients. Characterized by its relapsing nature, painful nodules, abscesses, and sinus tracts, predominantly in intertriginous regions, HS is associated with physical and psychosocial burden.1
Despite the expanding biologic armamentarium—including TNF-α inhibitors (adalimumab [Humira; AbbVie]), IL-17 inhibitors (secukinumab [Cosentyx; Novartis] and bimekizumab [Bimzelx; UCB]), and IL-36 inhibitors (spesolimab [Spevigo; Boehringer Ingelheim)—response rates remain modest. Only approximately 40% to 50% of patients achieve HS clinical response (HiSCR) at 12 weeks, largely due to poor improvement in draining tunnels.2,3
The IL-17 and IL-36 cytokine axes play pivotal roles in HS inflammation. Both pathways create a self-sustaining loop that drives keratinocyte activation, Th17 differentiation, and neutrophil recruitment, perpetuating tissue damage and tunnel formation.4-7 Inhibiting 1 pathway alone may be insufficient to halt disease progression, prompting exploration of dual-targeted biologic strategies.
This
Case Presentation
A 37-year-old man with a 12-year history of Hurley stage III HS presented with recurrent, painful, draining lesions of the scalp, axillae, and groin. Previous therapies—including isotretinoin, rifampicin, clarithromycin, and etanercept—failed to achieve disease control. His body mass index was 47.8 kg/m2.
The patient initially received secukinumab 450 mg subcutaneously once weekly for 3 weeks, with minimal improvement. After obtaining informed consent, intravenous recibokibart (anti–IL-36R monoclonal antibody) was initiated following a spesolimab proof-of-concept dosing schedule: 1080 mg at weeks 0, 1, and 2, followed by 1080 mg every 2 weeks from weeks 4 to 10, and secukinumab continued at weeks 0, 4, and 8.
Marked improvement occurred within 2 weeks (HiSCR 50), progressing to complete clearance (HiSCR 100) by week 10. Pain decreased from 8 to 2 on a visual analogue scale, and drainage resolved completely. Ultrasound imaging confirmed tunnel resolution and decreased inflammation across intertriginous sites. No adverse events were reported.
Clinical Implications
This report illustrates the potential of dual IL-17A and IL-36R blockade for severe, refractory HS. Both cytokines contribute synergistically to the disease’s chronic inflammatory loop, with IL-17 driving IL-36 production in keratinocytes and IL-36 amplifying Th17 and neutrophilic responses.6,7 Dual inhibition interrupts this feedback cycle, allowing more complete disease suppression.
Recibokibart, a novel anti–IL-36R antibody, has previously demonstrated efficacy in generalized pustular psoriasis.8 When combined with IL-17A blockade, it may extend benefit to HS phenotypes dominated by tunnels and abscesses.
Although this single case cannot establish safety or efficacy, it underscores a growing rationale for combination biologic therapy in treatment-resistant HS. Further controlled studies are needed to assess long-term outcomes, optimal dosing, and safety of concurrent cytokine inhibition.
Conclusion
Dual targeting of IL-17A and IL-36R represents an emerging therapeutic strategy for severe, refractory HS, especially cases unresponsive to single-pathway biologics. By addressing multiple inflammatory mechanisms simultaneously, such regimens may achieve deeper, more durable remission. Continued investigation into multicytokine blockade could reshape the treatment landscape for this challenging disease.
Jennifer Lightowler, MMSc, PA-C, is a board-certified dermatology physician assistant and medical writer in Connecticut.
References
- Sabat R, Alavi A, Wolk K, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa. Lancet. 2025;405(10476):420-438. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(24)02475-9
- Kimball AB, Jemec GBE, Alavi A, et al. Secukinumab in moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa (SUNSHINE and SUNRISE): week 16 and week 52 results of two identical, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2023;401(10378):747-761. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00022-3
- Alavi A, Prens EP, Kimball AB, et al. Proof-of-concept study exploring the effect of spesolimab in patients with moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Br J Dermatol. 2024;191(4):508-518. doi:10.1093/bjd/ljae144
- McCarthy S. Hidradenitis suppurativa. Annu Rev Med. 2025;76(1):69-80. doi:10.1146/annurev-med-051223-031234
- Patel KR, Lee HH, Rastogi S, et al. Association between hidradenitis suppurativa, depression, anxiety, and suicidality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83(3):737-744. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.11.068
- Krueger JG, Frew J, Jemec GBE, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: new insights into disease mechanisms and an evolving treatment landscape. Br J Dermatol. 2024;190(2):149-162. doi:10.1093/bjd/ljad345
- Narla S, Azzam M, Townsend S, et al. Identifying key components and therapeutic targets of the immune system in hidradenitis suppurativa with an emphasis on neutrophils. Br J Dermatol. 2021;184(6):1004-1013. doi:10.1111/bjd.19538
- Yu Y, Li J, Liu H, Sun Y, Zhang F. Dual blocking of IL17A and IL36R for the treatment of refractory hidradenitis suppurativa: a case report. Biologics. 2025;19:581-584. doi:10.2147/BTT.S558500
Articles in this issue
about 1 month ago
Understanding the Plethora of Shampoosabout 1 month ago
Fall Clinical 2025: Clinical Innovation and Precision Careabout 1 month ago
A Personal Journey With Chronic Spontaneous Urticariaabout 1 month ago
The Year Without a DermatologistNewsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.