
A recent study found states' Medicare per-beneficiary spending between actinic keratosis and skin cancer differs widely.
Ilya Petrou, MD, is a contributing writer for Dermatology Times.

A recent study found states' Medicare per-beneficiary spending between actinic keratosis and skin cancer differs widely.
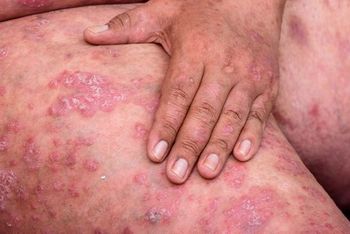
Several systemic therapies are currently available for the treatment of patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis. Biologics changed the game for treatment. Continued study of and innovation in IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors promise even better results, but clinicians need to understand each biologic in detail.
One expert says the action of demodex folliculorum and the composition of the symbiotic microbiota in the skin of patients with rosacea may provide valuable insights into the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of this widespread skin disease.
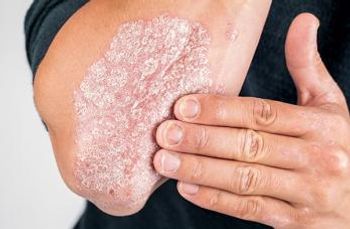
Several systemic therapies are available for the treatment of patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. Continued research has further elucidated the immunopathogenesis of the disease, leading to the development of novel biologic agents that are proving to more effectively and safely address moderate to severe psoriatic lesions.

Recently, PRAME (preferentially expressed antigen in melanoma) immunohistochemical staining has shown its usefulness in distinguishing benign from malignant melanocytic cell populations, offering another color to the canvas in the quest for a more definitive diagnosis of melanoma.

While Mohs micrographic surgery is well established as a safe and effective therapeutic modality in adult patients, it is not as commonly used in pediatric populations. There are unique challenges to performing Mohs surgery on pediatric patients, especially with patient cooperation. Multidisciplinary planning may be needed.
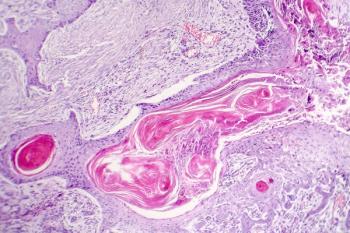
Investigators of a recent study found a 40-gene expression profile (40-GEP) test helps improve identification of high risk for metastatic disease in patients with cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC).

Researchers conducted a critical appraisal of a systematic review of six different smartphone apps and found little evidence that they are effective in self-monitoring or skin cancer detection, according to a recent study.

Dupilumab and JAK inhibitors are leading the way in atopic dermatitis treatment, but there are numerous clinical trials of both new biologics and new small molecule drugs, and future treatment regimens likely will utilize both.
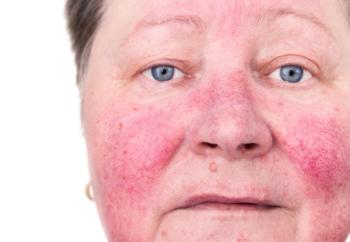
A recent paper discovered that the skin’s microbiota is closely associated with a number of systemic diseases, underscoring the need for clinicians to not only address the microbiota but also consider appropriate antibiotic therapy when contemplating treatment in rosacea patients.
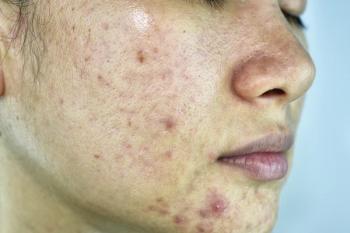
The popularity of laser and light devices has recently grown among acne patients, not only due to their e fficacy but also because treatments are quick and clean, says Michael H. Gold, M.D.
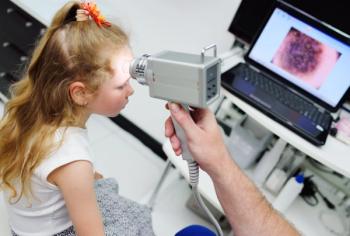
Read about the recent advancements in noninvasive imaging modalities that are making an impact on dermatological care.

Laser-assisted drug delivery used to fractionally ablate the target area prior to topical medical treatment can be useful in patients with widespread actinic damage, says this expert.

Dermatologists should work to gain a better understanding of immunologic pathways as well as the mechanisms of new and evolving immunotherapies, as these are key for understanding many current and emerging melanoma treatments, one expert says.

Better awareness in disease progression and improved understanding of field cancerization has shifted the thinking in management of patients with squamous cell carcinoma.
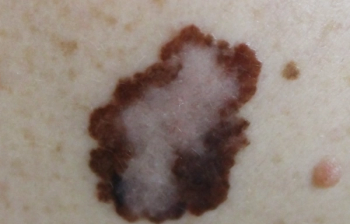
Sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) has classically been performed for regional disease control and to hopefully prevent disease metastasis; however, according to this expert, there has not been any good evidence to support this practice.

Molecular assays have been proven to assist in the diagnosis and prognosis of malignant melanoma. One expert expects that these molecular assays will play a central role in the future treatment and management of malignant melanoma.

Continued psoriasis research has led to a translational revolution in inflammatory skin diseases. As a result, there are now a number of safer and more effective medications that can address a growing list of common immune-mediated skin diseases, such as atopic dermatitis, alopecia areata, vitiligo, hidradenitis suppurativa, acne, and rosacea.
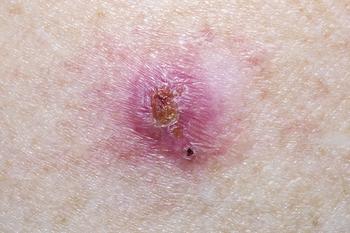
Superficial radiation therapy is experiencing a renaissance in dermatologic therapy due to the modernized equipment and updated guidelines, as well as excellent treatment outcomes for patients with NMSC which rival those seen with other approaches, including Mohs surgery.

Staphylococcus aureus infections are becoming more challenging to treat due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). A better understanding of cutaneous immune mechanisms will identify specific immune mechanisms to target for future vaccines and immunotherapies to ultimately address this serious public health threat.
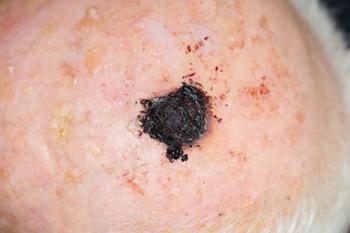
The cutaneous side effects of targeted therapies and immunotherapy for melanoma can complicate treatment and become a burden to patients. Dermatologists must aggressively address these side effects for a more ideal management and better quality of life for their melanoma patients.

Protease modulating therapies are used to assist in venous leg ulcer closure, but a recent review suggests that physicians should reexamine the biomarker's role in targeted chronic wound healing therapies.

Longer, more in-depth consultations with dermatologists, nursing staff, physician assistants could improve outcomes in psoriasis.

In this article, we review the American Academy of Dermatology treatment guidelines for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma.