Ixekizumab at three years holds well in psoriasis
Key Takeaways
- Ixekizumab treatment for plaque psoriasis showed no unexpected safety signals over three years, with no increased risk of cardiovascular disorders or malignancy.
- Infections were the most frequent adverse events, but were generally mild, manageable, and did not increase over time.
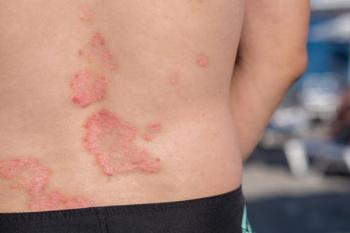
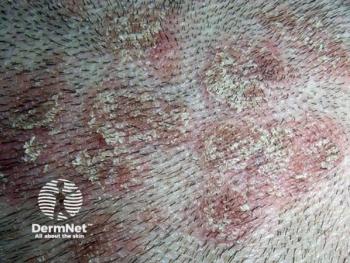
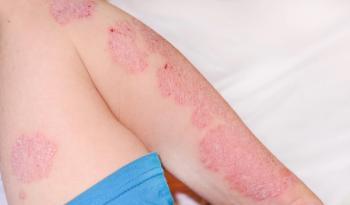
A review of more than 5,000 patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who were treated with ixekizumab over three years, shows no unexpected safety signals.
A review of more than 5,000 patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who were treated with
The review, published in the September issue of the Journal of European Academy of Dermatology & Venereology, examines treatment-associated adverse effects.
Plaque psoriasis is associated with a long list of comorbidities, such as cardiovascular disorders. And, biologic treatments have risks of their own, such as malignancy, but in this review,
As in previous reports, including a review of seven studies incorporating treatment of up to 60 weeks that was published in the March 2017 Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, infections were the most frequent adverse event associated with treatment affecting 28.7 patients per 100 patient-years. Most infections were mild to moderate and manageable.
"It’s reassuring to know that the risk of infection doesn’t increase over time. It’s also great to know that the inflammatory bowel issue associated with IL-17 blocking drugs is a rare phenomenon and not something that becomes common with long-term use," said Steven R. Feldman, M.D., Ph.D., a dermatologist with Wake Forest University School of Medicine in North Carolina who was not associated with the study.
“We have already come to expect that IL-17 blockade is an excellent way to control psoriasis, providing an extraordinary level of efficacy with an excellent safety profile," Dr. Feldman said.
Consistent with what is known about interleukin (IL)-17A inhibition and mucosal immunity, mucocutaneous candidiasis was the most common type of opportunistic infection reported. Diagnosis of latent tuberculosis caused 17 patients (0.3 percent) to withdraw from studies, although authors noted that false-positive tuberculosis test findings are common in populations with a low risk of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection.
"There were no cases of clinically active tuberculosis in the entire ixekizumab clinical development programme, including in patients with latent tuberculosis and patients with previously treated tuberculosis," the authors wrote. The incidence rate of injection-site reactions in the combined study population held steady or decreased over time.
Patients with psoriasis face a higher risk of inflammatory bowel disease. However, incidence rates of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis after three years of ixekizumab exposure were 0.0 per 100 patient years and 0.1 per 100 patient years, respectively.
Research has shown that during psoriatic inflammation, production of IL-17A increases in systemic circulation and may play a role in the development of depression. However, two pivotal ixekizumab trials showed that treatment with ixekizumab provided greater improvements in depression symptoms than placebo did.
In the present review, the cumulative rate of suicidal ideation or behavior decreased from 1.39 per 1,000 patient years (derived from the 2017 JAAD review) to 1.8 per 1,000 patient years. Langley et al. recorded 23 fatalities over 12,061.5 total patient years of ixekizumab exposure. However, most deaths occurred secondary to cardiovascular disorders, in patients with background risk factors, and no deaths were considered related to ixekizumab or suicide.
Among the combined study population, 3,787, 3,162 and 1,659 patients underwent treatment for at least one, two and three years, respectively. Median ixekizumab exposure was 883 days. The most frequently reported treatment-emergent adverse events were nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infections, injection-site reactions, headaches and arthralgia.
Given the chronic nature of psoriasis, wrote Langley et al., long-term data beyond their analysis are needed to fully characterize ixekizumab's safety profile in plaque psoriasis. While clinical trials strive to be as representative as possible of routine clinical populations, differences may still exist. Safety findings from longer-term observational studies and postmarketing data will be helpful, the authors said, especially for rare conditions.
"While we know ixekizumab (Taltz, Lilly) is very effective and safe in the short run, having three-year data to know that it is safe over the long haul is important to both dermatologists and our patients. "These findings are reassuring. They will continue to support the move toward greater use of highly targeted treatments like ixekizumab,” Dr. Feldman said.
REFERENCE
Richard G Langley MD, Alexa B Kimball MD, Hidemi Nakagawa MD, et al. "Long-Term Safety Profile of Ixekizumab in Patients with Moderate-To-Severe Plaque Psoriasis: an Integrated Analysis from 11 Clinical Trials,"
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.