Next-generation therapies explore solutions other than laser treatments, and are less invasive, safer and require less downtime.

Next-generation therapies explore solutions other than laser treatments, and are less invasive, safer and require less downtime.

Half of patients are satisfied with their atopic dermatitis treatment and more than half of patients worry about topical steroid side effects, addiction and withdrawal, according to a recent study.

Recent literature shows associations between rosacea and numerous inflammatory gastrointestinal disorders.

Dermatology Times announces the winners of its inaugural Giants of Dermatology awards, with six recipients being recognized this year for their contributions to the field of dermatology.

Read how some experts are balancing both their own health as well as the health of their patients during the COVID-19 pandemic.

In this month's Legal Eagle article, David Goldberg, MD, JD, explains how to avoid an age discrimination lawsuit from a former employee in your office by bulletproofing human resources (HR) documentation.

A recent paper suggests younger children with acne vulgaris should be treated the same as adolescents. This includes utilizing combination therapies that may consist of topic retinoids, benzoyl peroxide and other nonantibiotic agents in combination with antibiotics.
Genetic polymorphisms may increase psoriasis susceptibility, according to a study that found patients who have the G allele in the JAK1 gene have twice the risk of developing psoriasis, and for those with the JAK3 allele, the risk rises nearly 2-fold.
Patients with acne should be screened for vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency, according to researchers of a recent study investigating vitamin D's link to acne.
The use of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) has grown in popularity over the past few years. Zoe Diana Draelos, MD, explains the anti-aging benefits of PRP and how it is impacting dermatology.
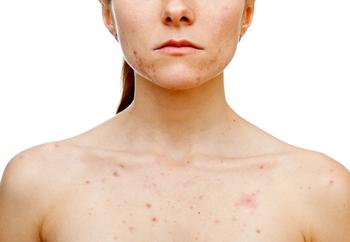
Perceptions of antibiotics and potential antibiotic resistance have caused some physicians to be wary of the drug class when prescribing an acne treatment regimen. However, narrow-spectrum antibiotics have shown a low propensity for development of antimicrobial resistance while also effectively treating acne.

B-cell lymphoma-2 inhibitor venetoclax has shown in clinical studies to improve symptoms with minimal toxicity in patients with cutaneous blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN), an aggressive hematologic cancer that can be rapidly fatal without treatment.

A new artificial intelligence-powered diagnostic tool, Ros-NET, was able to accurately identify rosacea, making way for further development of the technology to aid in diagnosis of the skin condition, according to a recent study.
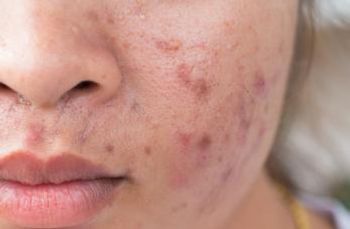
Spironolactone demonstrated notable safety and tolerability in females aged <21 years with refractory acne, according to a recent study from the Mayo Clinic.
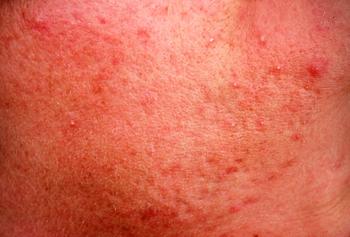
A recent study conducted by the National Rosacea Society reveals more rosacea patients are satisfied with their treatment, but highlights the need for treatment option awareness among older patient populations.