
Investigators suggest parents and clinicians should be mindful of children with suspected ACD with a history of exposure to jewelry, clothing, and belts with cobalt.
Armand Butera is the assistant editor for HCPLive. He attended Fairleigh Dickinson University and graduated with a degree in communications with a concentration in journalism. Prior to graduating, Armand worked as the editor-in-chief of his college newspaper and a radio host for WFDU. He went on to work as a copywriter, freelancer, and human resources assistant before joining HCPLive. In his spare time, he enjoys reading, writing, traveling with his companion and spinning vinyl records. Email him at abutera@mjhlifesciences.com.

Investigators suggest parents and clinicians should be mindful of children with suspected ACD with a history of exposure to jewelry, clothing, and belts with cobalt.
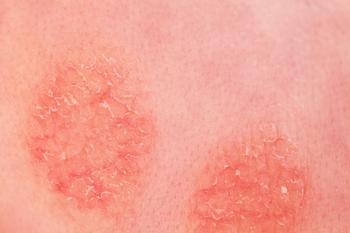
Investigators said that patient-reported outcomes from the 2 abrocitinib groups showed greater efficacy than the dupilumab and placebo groups.

Investigators reported that patients in the vitiligo group reported worse general health, and were willing to pay more than 40% of their income for a cure.

Investigators noted the treatment method was well tolerated in patients who could not safely use oral cyclosporine.

Combined therapies such as ultraviolet light and tab methotrexate were deemed effective in the management of vitiligo.

Investigators suggested the prevention of exposure during pregnancy could help control atopic dermatitis and other potential allergies in pediatric populations.

Patients treated with the monoclonal antibody had increased incidences of conjunctivitis, though many of these incidences were considered mild and were resolved by the end of the study.

Investigators recommended a treatment course of at least 1-2 months with medium strength to potent topical corticosteroids should be considered before dupilumab discontinuation in affected children and adolescents.

Investigators believe the new instrument could be generalized to other chronic inflammatory skin diseases in future studies.

The approval was supported by promising phase 3 data of the VOLTAIRE-X clinical trial.

Investigators also found that patients with alopecia areata were also had significant inflammatory immune injury and vitamin D deficiency when compared to healthy subjects.

Delgocitinib is the first and only topical JAK/STAT pathway inhibitor in Japan, and recent data suggests it is effective in the management of atopic dermatitis.

Investigators reported a significant difference in the expansion rate of the skin lesion area in patients with vitiligo in just 3 months of treatment.

Investigators added that the meaning of each laboratory marker is dependent on the drug that is being used for treatment.

Investigators write that methods such as dermatoscopy can result in early recognition of unstable patches and lead to appropriate medical treatment for patients with vitiligo.
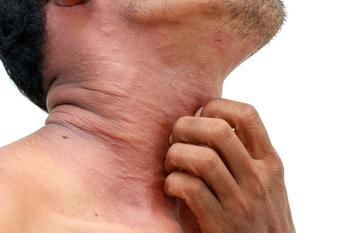
A new study sheds light on some of the atopic disease risks that are associated with early childhood and continue into midlife.

Though investigators called for more research on the biologic, recent data showed patients treated with bimekizumab recorded improved skin pain when compared to placebo and adalimumab.
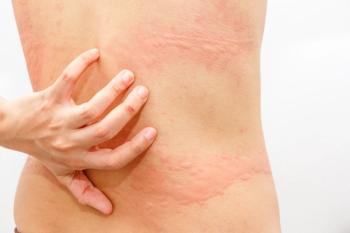
A recent statement by Regeneron noted that chronic spontaneous urticaria is the fifth disease associated with positive Phase 3 results involving the monoclonal antibody.

The newest FDA indication allows for greater distribution to younger but equally vulnerable immunocompromised patients.

Upadacitinib has shown promising results for a variety of diseases such as severe atopic dermatitis and psoriatic arthritis, but its future remains uncertain.

Published: September 29th 2021 | Updated:
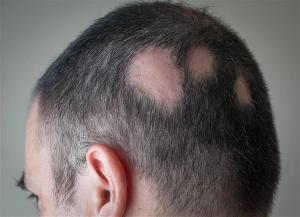
Published: October 6th 2021 | Updated:

Published: July 16th 2021 | Updated:

Published: September 17th 2021 | Updated: