Ruxolitinib for Treatment of Pediatric Atopic Dermatitis
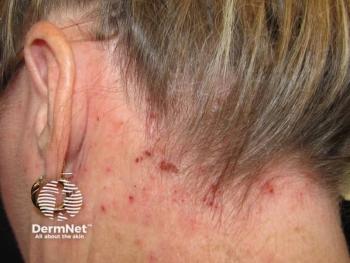
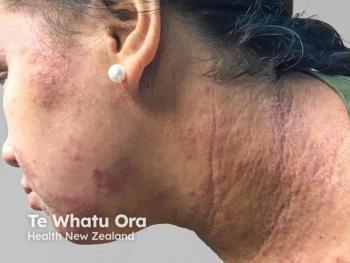
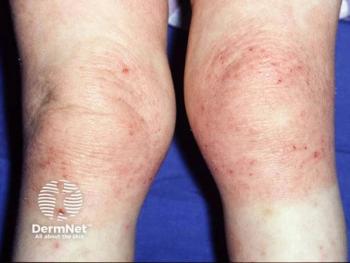
Panelists discuss how ruxolitinib cream demonstrated impressive efficacy in the TRU83 trial, with over 50% of patients achieving near-complete clearance at 8 weeks using the 1.5% formulation, while acknowledging that the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor’s broad mechanism makes its effectiveness unsurprising despite concerns about the boxed warning.
Children with atopic dermatitis who receive ruxolitinib cream treatment demonstrate impressive response rates that rival systemic medications, with clinical studies showing over 50% of patients achieving near-complete clearance after 8 weeks of treatment. The medication’s mechanism as a JAK1/2 inhibitor allows it to simultaneously block multiple inflammatory pathways, including IL-4, IL-13, and IL-31, essentially providing the benefits of several targeted therapies in a single topical application. This comprehensive approach to inflammation control explains why ruxolitinib consistently outperforms traditional treatments in clinical trials.
Patients using ruxolitinib cream experience significant improvements in skin clearance and quality-of-life measures, with the medication demonstrating an excellent safety profile when used appropriately. In the TRU83 pediatric trial, 36.6% of children using the 0.75% strength and over 50% using the 1.5% strength achieved investigator global assessment success at week 8, compared with only 10% with vehicle treatment. The most reported adverse effects were mild upper respiratory infections and nasopharyngitis, with no serious treatment-related adverse events occurring in the pediatric population.
Despite carrying a boxed warning similar to other JAK inhibitors, topical ruxolitinib maintains minimal systemic absorption when used according to prescribed guidelines, making serious adverse effects extremely unlikely. However, some families express concern about the warning label, leading to treatment discontinuation in some instances despite the medication’s demonstrated safety and effectiveness. Health care providers must balance thorough patient education about benefits and theoretical risks while emphasizing that topical application significantly reduces systemic exposure compared with oral JAK inhibitors.
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.