QUIZ RECAP: Dermoscopy and Melanoma Detection
Earlier this week, we shared our third Skin Cancer Awareness Month quiz. Review the answers and your responses below.
This week we asked the question:
Haven't taken our quiz yet? Pause before reading below and follow this link to complete it:
Below, we recap our third quiz and the correct answers to each question.
Question 1: What is the characteristic dermoscopic feature known as "negative pigment network" indicative of?
Response options:
- Benign nevus
- Melanoma
- Dermatofibroma
- Seborrheic keratosis
Correct response option: Dermatofibroma
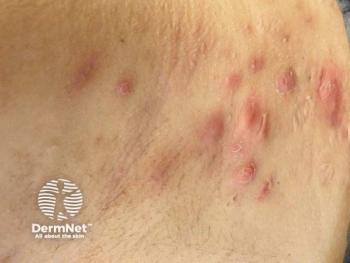
Dermatofibroma is characterized by an increase in fibrocytes in the dermis and sometimes the subcutis, and includes a mix of macrophages and inflammatory cells like lymphocytes, and rarely eosinophils, neutrophils, and plasma cells. Dermatofibromas typically present as firm, single or multiple hard papules, plaques, or nodules with a smooth surface and variable color, often occurring on the lower extremities and is dermoscopically characterized by a “negative” of the pigment network.1
Question 2: What is the significance of the "blue-white veil" in dermoscopy?
Response options:
- Presence of hemorrhage
- Indication of benign melanocytic lesion
- Suggestive of melanoma
- Presence of vascular structures
Correct response option: Suggestive of melanoma
A key diagnostic feature of melanoma in dermoscopy images is the blue-white veil, which consists of irregular, structureless blue areas with an overlying white "ground-glass" film.2
Question 3: What dermoscopic finding is suggestive of a seborrheic keratosis?
Response options:
- Eccentric hyperpigmentation
- Blue-gray dots and globules
- Branched vessels
- Hairpin vessels
Correct response option: Hairpin vessels
In irritated seborrheic keratosis, hairpin-like vessels may become elongated, twisted, and branched. These vessels can show up as dark red dots in flat lesion areas and can take on perfect "U" shapes or twisted "U" shapes. Typical hairpin vessels are surrounded by a whitish halo, which is the keratin around them.3
Question 4: Which dermoscopic structure is commonly seen in basal cell carcinoma (BCC)?
Response options:
- Blue-gray ovoid nests
- Regular pigment network
- Maple leaf-like structures
- Rainbow pattern
Correct response option: Blue-gray ovoid nests
A 2019 NCBI study identified the most common dermoscopic features of basal cell carcinoma (BCC) as follows: arborizing vessels in 59% of cases, shiny white structures in 49%, and large blue-grey ovoid nests in 34%.4
Question 5: True or False: The "3-point checklist" in dermoscopy is used to differentiate between benign and malignant lesions.
Response options:
- True
- False
- Partially true
- True only for melanocytic lesions
Correct response option: True
Dermoscopy screening for melanoma involves a 3-point checklist: assessing asymmetry (due to variations in pigment network thickness, tumor regression areas, or unevenly distributed pigment globules), identifying atypical pigment networks (with thick branches and lack of peripheral fading), and spotting blue-colored areas. If a lesion shows more than one of these features, it should be biopsied, monitored, or the patient referred to a dermatologist.5
References
- Zaballos P, Puig S, Llambrich A, Malvehy J. Dermoscopy of dermatofibromas: A prospective morphological study of 412 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144(1):75–83. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2007.8
- Celebi ME, Iyatomi H, Stoecker WV, et al. Automatic detection of blue-white veil and related structures in dermoscopy images. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2008;32(8):670-677. doi:10.1016/j.compmedimag.2008.08.003
- Ayhan E, Ucmak D, Akkurt Z. Vascular structures in dermoscopy. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90(4):545-553. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20153452
- Reiter O, Mimouni I, Dusza S, Halpern AC, Leshem YA, Marghoob AA. Dermoscopic features of basal cell carcinoma and its subtypes: A systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85(3):653-664. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.11.008
- Gniadecki R, Mourad A. Differentiating malignant melanoma from other lesions using dermoscopy [published correction appears in Can Fam Physician. 2019 Aug;65(8):531] [published correction appears in Can Fam Physician. 2019 Aug;65(8):532]. Can Fam Physician. 2019;65(6):412-414.
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.