- Dermatology Times, Considering Biologics and Shared Decision-Making in Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis, December 2025 (Vol. 46. Supp. 12)
- Volume 46
- Issue 12
From Scalp to Nails: Tailoring Biologic Therapy for Patients With Psoriasis
Key Takeaways
- Individualized treatment strategies are crucial, considering disease severity, lifestyle, prior responses, and comorbidities for effective psoriasis management.
- Regular monitoring of treatment efficacy and adverse events, especially infections like oral candidiasis with IL-17 inhibitors, is essential.
Explore real-world strategies with Leigh Ann Pansch, MSN, FNP-BC, DCNP, for managing psoriasis, emphasizing patient-centered care, and implementing individualized biologic treatment approaches.
At a recent
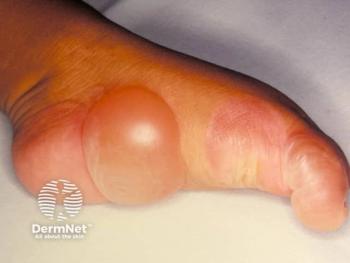
Case 1: A 40-Year-Old Man With Moderate Psoriasis
In this first case, a 40-year-old man presented with psoriasis affecting his scalp, arms, and lower legs (approximately 10% body surface area [BSA]), with moderate itch. The patient works as a park ranger with limited follow-up availability and prefers quick, effective treatments. The clinicians opted to initiate a biologic, specifically bimekizumab (Bimzelx; UCB). The IL-17 inhibitor can accommodate the patient's busy lifestyle and desire for rapid results, and the dosing every 8 weeks aligns with patient needs for convenience and quick efficacy.
Key considerations:
- Treatment escalation: The decision to escalate relies on objective measures (eg, Psoriasis Area and Severity Index [PASI], BSA) and the impact on quality of life.
- Risks of topicals: Topical treatments may be insufficient for extensive disease or difficult-to-manage sites, necessitating systemic therapy.
- Monitoring and safety: Close monitoring for adverse effects, such as oral candidiasis, is essential. Regular assessment of treatment response using PASI, BSA, and patient feedback guides ongoing management.
- Future management: If the patient experiences treatment failure or adverse events, the panel discussed switching options, considering efficacy, safety, and patient preferences.
Case 2: A 42-Year-Old Man With PsA and Nail Involvement
The second case involves a patient with long-standing plaque psoriasis (approximately 8% BSA) primarily on his arms and legs. Recently, he reported nail psoriasis (pitting and onycholysis), which can be more challenging to treat and significantly impacts his quality of life. The patient also previously used ustekinumab (Stelara; Janssen Biotech) for 2 years with waning efficacy. Here, Pansch and the attendees chose the IL-23 inhibitor risankizumab (Skyrizi; AbbVie), as it has proven effective for both skin and nail psoriasis.
Key considerations:
- Safety and comorbidities: The patient has a family history of ulcerative colitis, which may influence the choice of biologics.
- Patient preferences: He is also looking for a convenient dosing option (every 12 weeks) due to his lifestyle and ability to adhere to treatment.
- Monitoring and follow-up: Regular assessment of skin and nail responses (eg, PASI, Nail Psoriasis Severity Index scores) and vigilance for adverse effects is vital.
- Patient involvement: Shared decision-making, including discussion of risks, benefits, and patient desires, is emphasized to improve adherence and satisfaction.
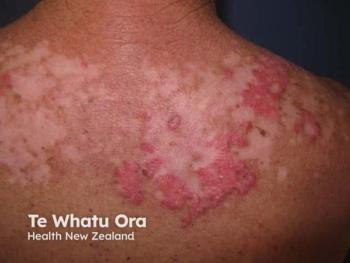
Case 3: A 49-Year-Old Woman With Scalp Psoriasis and Prior Biologic Use
The final case involved a woman with extreme itch and discomfort from psoriasis on her scalp and elbows that began 10 years ago. She had been using secukinumab (Cosentyx; Novartis) for 18 months with partial response on her elbows and minimal response on her scalp, noting that she was unhappy with the results. The panel discussed several treatment adjustments, including the possibility of increasing the dose, adding adjunctive therapies such as topical agents, or switching biologics. The decision involves evaluating outcomes, such as PASI scores, safety profiles, and patient-reported improvements.
Key considerations:
- Factors influencing biologic selection: Disease severity, previous response, safety profile, and mechanistic differences (eg, IL-17A vs IL-17A/F inhibition) are crucial.
- Switching dynamics: Switching within the IL-17 class (eg, from secukinumab to bimekizumab) may be guided by partial response or adverse effects. Switching mechanisms (eg, from IL-17 to IL-23 inhibitors) may be considered for refractory cases.
- Difficult-to-treat areas: Consider biologics with a rapid onset or higher potency for scalp involvement.
- Outside support: Monitor the impact on the patient’s mental health and turn to referrals for psychological support if needed.
Practice Pearls
The roundtable emphasized that a comprehensive, patient-centered approach is essential for optimizing disease management. Across all 3 cases, several key practice pearls emerged that underscored effective treatment of psoriasis:
- Monitoring and safety: Regular assessment of treatment efficacy and adverse events is crucial, with particular attention to infections, such as oral candidiasis, associated with IL-17 inhibitors.
- Mechanistic considerations: Understanding differences in biologic mechanisms guides both initial choice and switching strategies.
- Patient-centered approach: Engaging patients through shared decision-making, considering lifestyle, treatment convenience, and preferences, enhances outcomes.
- Treatment escalation and switching: Clear criteria for treatment failure, combined with an individualized approach to modifying therapy, help optimize disease control.
Final Thoughts
Pansch highlighted the value of events like these, as they allow providers to enhance their decision-making skills through the discussion of real-world cases, clinical data, and treatment guidelines. Peer-to-peer learning was emphasized through the exchange of diverse perspectives and practical insights that can be directly applied to patient care.
“I think the patient cases presented allowed an open dialogue amongst all the attendees in an environment that fostered honesty. I felt the attendees learned from each other, and I’ve received some notes from attendees already indicating they’ve tried something new [that] was discussed at the Case-Based Roundtable,” Pansch said.
Articles in this issue
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.