- Dermatology Times, October 2023 (Vol. 44. No. 10)
- Volume 44
- Issue 10
Acne Conglobata: An Overview and Effective Management Strategies
The impact of acne conglobata on individuals underscores the crucial role dermatologists play in providing effective diagnosis, treatment, and emotional support.
Although most acne cases are mild or moderate and tend to resolve with treatments that are well-known in a dermatology armamentarium, some individuals face a rare and severe variant known as acne conglobata. This article provides a comprehensive understanding of the condition and its clinical presentation as well as effective management strategies available for individuals grappling with this severe form of nodulocystic acne.1
Understanding Acne Conglobata
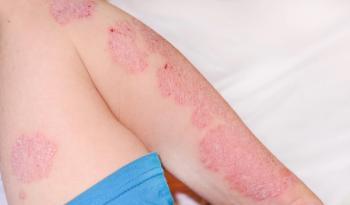
Acne conglobata is a severe and relatively uncommon form of acne vulgaris. Its defining characteristic lies in the formation of large, painful, and interconnected nodules and abscesses beneath the skin’s surface. Unlike typical acne, which primarily affects adolescents, acne conglobata tends to emerge during younger adulthood, usually before age 40 years. This rarity makes it even more important to understand its complexities and develop appropriate management strategies.2
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation
The hallmark of acne conglobata is the development of deep, inflamed nodules and abscesses that extend far beyond the scope of typical acne pustules. These lesions can cause profound scarring and disfigurement, which often leads to emotional distress in affected individuals. The pain and discomfort associated with acne conglobata are exacerbated by the size and depth of these lesions, which can manifest on various parts of the body, including the face, chest, back, and extremities.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
Diagnosing acne conglobata necessitates a meticulous examination. Patients present with “tender, disfiguring, double or triple interconnecting comedones, cysts, inflammatory nodules, and deep burrowing abscesses on the face, shoulders, back, chest, upper arms, buttocks, and thighs.”1 The diagnostic process involves a comprehensive approach. Laboratory tests may be required to supplement the clinical assessment. Especially in males, evaluating hormone levels can provide insight into underlying hormonal imbalances that contribute to acne conglobata. Secondary bacterial infections are common in acne conglobata, making cultures and infectious screenings essential.
Management Strategies
Managing acne conglobata is challenging. With a comprehensive approach, patients can achieve remarkable improvements in their condition. Effective management strategies encompass a range of medical treatments, surgical and procedural interventions, and vital psychological support.
1. Medical Treatments
Oral isotretinoin is considered the gold standard for severe acne. Oral isotretinoin can significantly reduce oil production by shrinking sebaceous glands and preventing clogged pores.
Antibiotics may be prescribed to control bacterial infections and inflammation, particularly in the early stages of treatment. Oral or intralesional steroids can provide rapid relief from inflammation and pain associated with acne conglobata. In cases where hormonal imbalances are a contributing factor, hormonal therapy may be beneficial. This is especially relevant for women with hormonal irregularities that contribute to the condition. Topical retinoids can be used in combination with other treatments to help unclog pores and reduce inflammation.
2. Surgical and Procedural Interventions
Dermatology clinicians may perform incisions and drainage to alleviate pain and eliminate pus from abscesses. Superficial chemical peels can improve skin texture and reduce scarring, enhancing the overall appearance of the affected areas. Laser treatments can target and shrink sebaceous glands, thus reducing oil production and improving the appearance of the skin. Surgical removal of large, persistent nodules may be necessary to prevent further complications.
3. Psychological Support
A patient’s journey with acne conglobata can be emotionally taxing, often affecting their self-esteem and mental well-being. Therefore, psychological support is a crucial component of effective management. Engaging in counseling or joining support groups can help individuals cope with the emotional toll of acne conglobata. Knowledge is also power. Patients should be educated about the condition, its treatment options, and the significance of adhering to prescribed medical regimens.
Preventive Measures
Although preventing acne conglobata may not always be possible, certain lifestyle modifications can aid in managing the condition and reducing risk of recurrence. A skin care routine should include a mild, noncomedogenic cleanser to keep the skin clean without overdrying or exacerbating irritation, as well as sunscreen with a broad-spectrum sun protection factor to protect the skin from harmful UV rays and prevent postinflammatory hyperpigmentation. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can contribute to overall skin health. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help alleviate the emotional burden associated with acne conglobata. Ensuring sufficient rest is essential for overall skin health, because lack of sleep can exacerbate skin conditions.
Conclusion
Acne conglobata is a formidable dermatologic condition that can profoundly affect an individual’s physical and emotional well-being. However, with the appropriate medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and psychological support, patients can achieve significant improvement in their skin condition and overall quality of life. The impact of acne conglobata on individuals underscores the crucial role dermatologists play in providing effective diagnosis, treatment, and emotional support, enabling patients to regain their skin health and confidence.
Isabella Tan is from Potomac, Maryland, and is a rising medical student at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School in New Brunswick, New Jersey.
References
1. Hafsi W, Arnold DL, Kassardjian M. Acne conglobata. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Accessed September 15, 2023.
2. Greywal T, Kusari A, Han AM, et al. Severe acne and its variants: Exploring its natural history and heritability. Pediatr Dermatol. 2022;39(4):535-540. doi:10.1111/pde.14990
Articles in this issue
about 2 years ago
Discovering Dermatology Times: October 2023over 2 years ago
Understanding Your Investment in a Financial Adviserover 2 years ago
Preparing Your Patient to Ask for ADA Workplace Accommodationsover 2 years ago
Artificial Intelligence: Friend or Foe?over 2 years ago
October Pipeline PreviewNewsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.