Journal Digest: October 17, 2025
Key Takeaways
- Pediatric HS is associated with dermatologic, metabolic, and autoimmune comorbidities, with Down syndrome showing a strong link.
- HS significantly affects sexual health, with dysfunction rates up to 71.8%, influenced by pain, odor, and psychological factors.
This review of the latest dermatologic studies highlights new research on hidradenitis suppurativa, including associated pediatric comorbidities, CO2 laser treatment, impact on sexual health, and more.
Pediatric Dermatology | Comorbidities of Pediatric Patients With Hidradenitis Suppurativa in the Emergency Department Setting: A Cross-Sectional Study
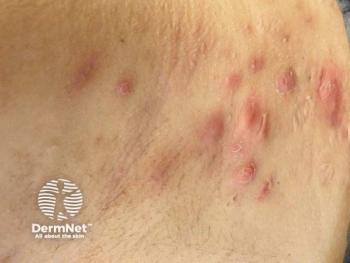
This cross-sectional study analyzed data from the Nationwide Emergency Department Sample (2006–2019) to identify comorbidities associated with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) in pediatric patients. Using ICD codes, researchers examined over 31,000 pediatric ED visits for HS, revealing significant associations with 17 comorbid conditions. These included dermatologic disorders (acne, pilonidal cyst, pyoderma gangrenosum), metabolic conditions (obesity, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, PCOS), and autoimmune diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis). Psychosocial conditions such as anxiety and depression appeared more common but were not significantly associated after adjusting for confounders. Down syndrome showed a notably strong association. The findings suggest that pediatric HS is linked with a broad range of systemic and dermatologic comorbidities, especially metabolic and autoimmune disorders.1
Dermatologic Therapy | The Impact of Hidradenitis Suppurativa on Sexual Health: A Systematic Review
This systematic review examined the impact of HS on sexual health, focusing on both male and female patients. Analyzing 13 studies involving over 46,000 HS patients, the review found a high prevalence of sexual dysfunction, affecting 42% to 71.8% of individuals. Female patients commonly reported greater sexual distress, while males experienced higher rates of erectile dysfunction. Interestingly, disease severity (e.g., Hurley stage) did not consistently correlate with worse sexual function. Instead, pain, odor, and the presence of genital lesions were stronger contributors to sexual dysfunction. Psychological factors, including depression and anxiety, were also significantly linked. While some comorbidities and lifestyle factors (like smoking or alcohol use) influenced outcomes, their roles were complex. Future research should focus on behavioral impacts, infertility, and the experiences of HS patients' partners to improve overall care strategies.2
Clinical Case Reports | Management of Severe Bilateral Axillary Hidradenitis Suppurativa in a Resource-Limited Setting: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
This case report details the successful management of severe bilateral axillary HS in a resource-limited setting using wide local surgical excision. The patient, a 37-year-old man with a 2-year history of recurrent discharging sinuses, did not respond to medical therapies, including antibiotics and corticosteroids. Due to limited access to biologic treatments and the presence of complicating factors such as obesity, diabetes, and hepatitis B, surgery was pursued. Complete excision of diseased tissue followed by secondary intention healing led to full recovery without recurrence at 12 months. The report emphasizes that even in low-resource environments, HS can be effectively treated with basic surgical techniques and diligent postoperative care.3
Japanese Dermatological Association | Familial Hidradenitis Suppurativa on the Island of Crete: Distinct Patterns in Clinical Characteristics
This study examined differences in clinical characteristics between HS patients with and without a first-degree family history (FH) of the disease on the island of Crete. Among 170 adult HS patients, 30% reported a familial link. Those with a FH were significantly more likely to be female, experience earlier disease onset, and be classified at Hurley stage 2. Additionally, familial HS patients had higher rates of atopy (25.5% vs. 12.6%) and psychiatric disorders (33% vs. 5.9%). A notable association was also found between female gender and the presence of atopic conditions. These results suggest that familial HS may present with a distinct clinical profile, potentially influenced by genetic or environmental factors.4
Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology & Venereology | Largest Prospective Study of CO2 Laser Treatment in Hidradenitis Suppurativa Patients Showing Improved Quality of Life
This prospective study—the largest of its kind—evaluated CO₂ laser treatment in 53 HS patients, focusing on patient-reported outcomes, complications, and recurrence. Over a 12-week follow-up, CO₂ laser treatment significantly improved quality of life, as shown by reductions in Dermatology Life Quality Index (ΔDLQI −3.5, p < 0.0002) and HiSQOL scores (ΔHiSQOL −7.1, p < 0.006). Complications were generally low: infection (5.8%), bleeding (21%), and sensory disturbances (7.7%). However, 26.9% experienced recurrence at the edge of the treated area, and another 26.9% had prolonged wound healing (>12 weeks), which was more common in patients with higher BMI and those on biologics. Recurrence and healing complications were also more frequent in certain anatomical sites (e.g., axilla).5
References
1. Hailemichael R, Martin SA, Hwang A, Riley JM, Flood KS, Ren Z. Comorbidities of Pediatric Patients With Hidradenitis Suppurativa in the Emergency Department Setting: A Cross-Sectional Study. Pediatr Dermatol. Published online October 13, 2025. doi:10.1111/pde.70054
2. Nigro, Alexandra R., Osman, Alim, Cleland, Elissa, Povelaitis, Michael, Handler, Marc Z., The Impact of Hidradenitis Suppurativa on Sexual Health: A Systematic Review, Dermatologic Therapy, 2025, 2247169, 15 pages, 2025. https://doi.org/10.1155/dth/2247169
3. Mosha N, Mremi A, Mshana J, Kini LC, Mavura D, Jemec G. Management of Severe Bilateral Axillary Hidradenitis Suppurativa in a Resource-Limited Setting: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Clin Case Rep. 2025;13(10):e71176. Published 2025 Oct 6. doi:10.1002/ccr3.71176
4. Koumaki D, Gregoriou S, Evangelou G, et al. Familial Hidradenitis Suppurativa on the Island of Crete: Distinct Patterns in Clinical Characteristics. J Dermatol. Published online October 7, 2025. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.17951
5. Daugaard, C.A., Schøsler, L.W., Rasmussen, M.K., Kibsgaard, L., Meszes, A., Høgsberg, T. and Bertelsen, T. (2025), Largest Prospective Study of CO2 Laser Treatment in Hidradenitis Suppurativa Patients Showing Improved Quality of Life. JEADV Clinical Practice. https://doi.org/10.1002/jvc2.70110
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.