Innovations Transforming How We Manage HS
Key Takeaways
- HS is often misdiagnosed, leading to delayed treatment and severe complications, including scarring and psychosocial distress.
- Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial to prevent disease progression and improve long-term outcomes for HS patients.
Discover the latest insights on hidradenitis suppurativa treatment, emerging therapies, and the importance of compassionate care for patients.
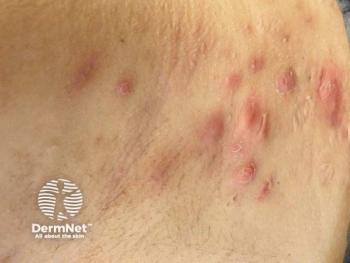
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic, painful, and often under-recognized inflammatory skin condition that can profoundly impact patients’ physical, emotional, and social well-being. HS typically presents with recurrent, inflamed nodules, abscesses, and sinus tracts, most commonly in areas such as the underarms, groin, and buttocks. The disease often goes undiagnosed for years, leaving patients to suffer with both physical discomfort and psychosocial distress, including anxiety, depression, and social isolation.1
At the
Recognizing the Challenges of HS
HS is frequently misdiagnosed or overlooked, with patients often waiting 5 to 7 years before receiving an accurate diagnosis. This delay can lead to the development of permanent sinus tracts, extensive scarring, and a worsening of chronic inflammation.2 Beyond the physical manifestations, HS carries a heavy psychosocial burden. Patients often experience anxiety, depression, and feelings of stigma due to the visible nature of the disease and its impact on daily activities and personal relationships.
Neita emphasized the importance of a holistic approach to care. “Clinicians need to recognize not only the visible lesions but also the associated comorbidities, including metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, and other inflammatory conditions,” she explained. Comprehensive care requires looking beyond the skin to address the overall health and quality of life of the patient.
The Critical Importance of Early Intervention
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial in preventing the progression of HS. Neita highlighted that there is a “window of opportunity” during which prompt treatment can prevent severe tissue damage, sinus tract formation, and extensive scarring. Early intervention not only reduces the frequency and severity of flares but also improves long-term outcomes and enhances quality of life.
Timely treatment also enables clinicians to implement a combination of medical and surgical strategies tailored to the patient’s needs, ensuring that the disease is managed effectively before complications become irreversible.
Current and Emerging Therapies
The HS treatment landscape has evolved significantly in recent years. Currently, FDA-approved options include biologic therapies, primarily IL-17 inhibitors, which target the inflammatory pathways driving the disease. In addition to systemic therapy, surgical interventions are an important component of care. Procedures like de-roofing for acute abscesses are preferred over traditional incision and drainage, which often leads to recurrence or poor healing.
Exciting new therapies are on the horizon, offering hope for patients who have previously had limited treatment options:
- Oral JAK inhibitors, which target specific inflammatory pathways
- Porvorcitinib and other novel agents under investigation
- Additional biologics and small-molecule therapies designed specifically for HS
These emerging therapies promise to expand options for personalized treatment and improve outcomes for patients with moderate to severe disease.
Compassionate Care and Shared Decision-Making
A recurring theme of the discussion was the importance of empathy in HS management. Many patients have been dismissed, undertreated, or mistreated by prior health care providers. Neita emphasized that effective care combines clinical expertise with understanding and compassion. “Shared decision-making is essential,” she noted, “because so many HS patients have been suffering in silence and need to feel heard and understood.”
Clinicians must also recognize the psychosocial toll of HS and integrate supportive care, including counseling and patient education, into their management plans.
Raising Awareness and Community Education
Neita shared her experience speaking at Atlanta City Hall, where she educated city employees about HS and interviewed a patient advocate about her personal journey. Awareness and education are critical, as many patients only find relief when they learn the name of their condition. Neita encouraged health care professionals and advocates to use every available platform, including social media, local events, or clinic outreach,to educate the public and reduce the stigma surrounding HS.
Looking Ahead
The future of HS management is promising, with multiple new therapies in development that target inflammation more precisely and effectively. Oral agents such as porvorcitinib, along with emerging biologics and small molecules, are expected to transform the treatment landscape. Combined with early diagnosis, proactive management, and compassionate patient-centered care, these advances have the potential to dramatically improve long-term outcomes and quality of life for patients with HS.
HS remains a complex and challenging condition, but through continued innovation, education, and empathy, clinicians can make a meaningful difference in the lives of those living with this disease.
References
Virone M, Zappia E, Di Caro A, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: state-of-the-art review and update. Dermatol Reports. Published online August 27, 2025. doi:10.4081/dr.2025.10328
Klufas DM, Ojute F, Shochat G, Naik HB. Diagnosis and management of hidradenitis suppurativa: a review for the emergency clinician. Emerg Med J. 2025;42(3):202-208. Published 2025 Feb 21. doi:10.1136/emermed-2024-213949
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.