In Review: Looking Back at Some of 2023's Largest Studies in Dermatology
Dermatology Times is reviewing some of the newest and largest studies coming out of this year.
Acne
Data published in Nucleic Acids Research builds on previous studies investigating the benefits of sarecycline for acne vulgaris compared to other antibiotics.
Yale School of Medicine researchers found tetracycline-class antibiotics were the most prescribed acne treatment for adult female patients between 2002 and 2016.
Aesthetics
Steven Dayan, MD, FACS, first author behind a recent study involving high rates of patient satisfaction following treatment with botulinum toxin, discusses the importance of placing patient satisfaction at the forefront of cosmetic dermatology.
Sachin Shridharani, MD, discusses the results of a recent Allergan Aesthetics study exploring the efficacy of onabotulinumtoxinA in treating platysma prominence.
Greg Pierce of Synchrony discusses CareCredit's Path to Care study and its findings related to cost and finance considerations for cosmetic dermatology patients.
Alopecia
The findings of this cross-sectional study indicate alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, and alopecia universalis is more common in people of color, particularly Asian Americans.
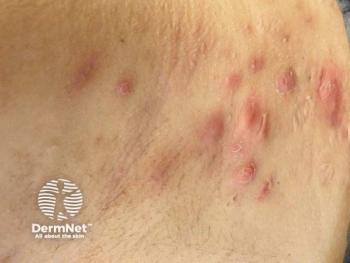
Dermatitis
Cytokine-expressing genes were silenced in a recent Vanderbilt University Medical Center study.
Researchers link proximity to heavy traffic and risk of atopic dermatitis in new study.
A single-site study involving an adult cohort with atopic dermatitis saw significant itch improvement.
New data from Dermavant showed high levels of efficacy and statistical significance for the topical cream, which is expected to have an sNDA on file with the US FDA in early 2024.
The TRuE-AD3 study met its primary endpoint of IGA-TS improvement from baseline at week 8.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Incyte announces that its study of povorcitinib revealed sustained and durable efficacy after 1 year.
A key factor associated with delayed diagnosis for non-White patients is the lack of awareness that their symptoms are associated with a treatable medical condition, according to Oma Agbai, MD, and Lisa Nyanda-Manalo, MD.
The OSIRIS open-label study resulted in a reduction of pain and improvement in quality of life for participants.
The IL-17A inhibitor did not meet its phase 2b/3 clinical trial primary end point.
Psoriasis
Union therapeutics is also developing the drug for treatment of atopic dermatitis and hidradenitis suppurativa.
The year-long study gives insight to the treatment’s efficacy and safety of durability.
In the PERSIST study, improvements were sustained through week 104.
The study is the only large-scale dermatologic study to prospectively generate insights into skin conditions among patients of racial and ethnic minority groups.
Rosacea
Based on the positive topline phase 3 results, Journey Medical plans to submit a New Drug Application to the FDA in the second half of 2023.
Skin Cancer
A study published in Future Medicine finds consistent use of the treatment is difficult for patients to maintain in a real-world setting.
Researchers were unable to determine a definite correlation.
Verrica Pharmaceuticals is developing a potentially first-in-class oncolytic peptide.
Vitiligo
The investigational oral JAK1 inhibitor showed promising results for vitiligo patients.
A real-world retrospective analysis also found that among patients receiving treatment, most were unlikely to use more than 1 treatment or switch to an alternative treatment during the first year of diagnosis.
Other
Researchers anticipate that upwards of 10,000 adults with various dermatologic conditions will partake in the study.
Notice any major studies we may have missed in our recap? Email our team at
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.