Phase 4 study program expands sizeable database on Metvix PDT
The phase 4 studies are designed to gather additional information on Metvix PDT compared with alternative treatments along with the use in specific patient populations and in new ways.
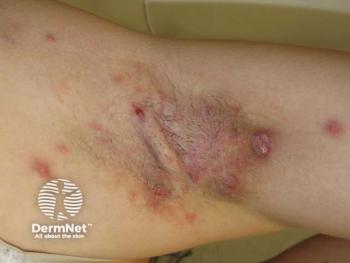
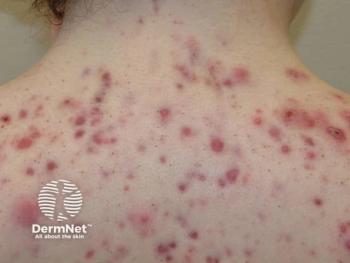
An extensive phase 4 researchprogram is under way to further evaluate Metvix PDT (Galderma) in the treatment of actinickeratoses (AKs) and basal cell carcinomas (BCCs).
Indications For treating BCCs and for the AK indication in the U.S., a series of two treatments are performed one week apart. In Europe, a single treatment repeated at three months if necessary has been approved for treating AKs.
"There is already a substantial existing database to demonstrate Metvix PDT is a safe and effective treatment with some advantages for clearing AKs and both nodular and superficial BCCs. However, PDT is a relatively new therapy in dermatology that has yet to become well established in clinical practice. The results of these trials will enhance our understanding of the efficacy and safety of Metvix PDT for these precancerous and cancerous lesions in a broader range of patients, help us to better define its therapeutic role and thereby provide clinicians with the additional evidence-based medicine they may need to select this treatment modality with confidence," says Pascale Soto R.Ph., head of the phase 4 study group, Galderma R&D, Sophia Antipolis, France.
Clearance rates In premarketing phase 3 clinical trials where response rates were evaluated at three months post-treatment, Metvix PDT resulted in high complete clearance rates when used to treat AKs of the face and scalp (89 to 91 percent), nodular BCCs (91 percent), and superficial BCCs (97 percent).
Based on head-to-head comparisons, its efficacy was superior to placebo-PDT for treatment of AKs, at least as effective as cryotherapy in treating AKs or superficial BCCs and comparable to excision surgery for nodular BCCs.
However, Metvix PDT is a noninvasive treatment, and it had an advantage relative to cryotherapy and surgery for resulting in a better cosmetic outcome when that endpoint was assessed after 12 or 24 months by patients and investigators.
Multiple aims The phase 4 studies are designed to gather additional information on Metvix PDT compared with alternative treatments along with the use in specific patient populations and in new ways.
One of the phase 4 AK studies is investigating Metvix PDT for the treatment of lesions located at anatomic sites other than the face and scalp using cryotherapy as an active comparator. A second AK study is assessing patient preference and lesion response with Metvix PDT in comparison to cryotherapy. This trial is entering patients with multiple lesions who are serving as their own controls. Selected target lesions in each individual are being assigned to treatment with either Metvix PDT or cryotherapy.
"In several premarketing studies, patient surveys demonstrated preference for Metvix PDT compared with cryotherapy, surgical excision and topical chemotherapy among individuals who had been treated previously with those options," Ms. Soto tells Dermatology Times. "We think it is very valuable to determine the patient's perspective on Metvix PDT when it can be simultaneously compared with an alternative therapy."
A further phase A further phase 4 AK study is examining strategies for minimizing treatment-associated pain and improving postoperative management.
Rolf-Markus Szeimies, M.D., Ph.D., professor of dermatology, University of Regensburg, Germany, is an investigator in this and two other phase 4 studies. He also participated in AK premarketing clinical studies.
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.