- Dermatology Times, December 2022 (Vol. 43. No. 12)
- Volume 43
- Issue 12
Holistic Treatment for the Management of Atopic Dermatitis
Patients are finding relief in alternative therapy for the chronic skin disease.
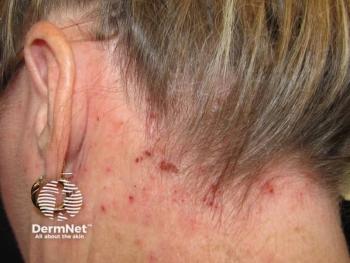
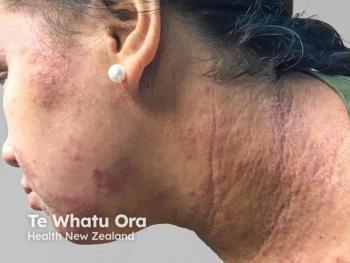
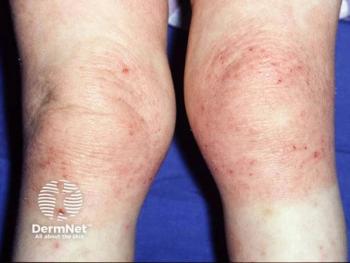
Atopic dermatitis (AD), often called atopic eczema, is the most common inflammatory skin condition, affecting people of all ages, from newborns to adults over 65 years of age. Around 230 million people live with the disease worldwide.1 The disease is characterized by itchy, dry, and cracked skin.
The management of AD usually depends on long-term adherence to prescription medicines and avoidance of environmental triggering factors. Because medications only address the physical ailment and often come with adverse effects, many patients with AD prefer seeking treatment options beyond standard medications. Holistic medicine provides one such approach to managing the disease.
What Is Holistic Treatment?
Holistic treatment is an approach that focuses on the patient as a whole–body, mind, and spirit––in the quest for optimal health, rather than merely treating a particular disease. It is based on the philosophy that optimal health can be achieved by attaining a balance in life. Holistic practitioners believe that our body parts are interdependent; if one part is hurt, the other parts will also be affected, negatively impacting overall health. The practitioners use both Western medicines and alternative therapies, focusing on alleviating the cause of the condition rather than just managing the symptoms. Some of the commonly used holistic treatments for AD are discussed in this article.
Holistic Treatments for Atopic Dermatitis
Natural oils: Virgin coconut oil provides an inexpensive, safe alternative option in the management of AD. It has been used to moisturize the skin for centuries. It consists of triglycerides, polyphenols, and fatty acids as main components and has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antibacterial properties, promoting wound healing and moisturizing AD skin.2 According to results of a study published in the Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine, the anti-inflammatory properties of virgin coconut oil help suppress inflammatory markers and enhance the skin barrier function, thereby protecting the skin.3
Sunflower seed oil also is known for its anti-inflammatory properties among patients with AD. It contains linoleic acid that activates peroxisome proliferative-activate receptor-α, thus decreasing inflammation and improving skin barrier function.4
Acupuncture: Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) practice that involves the penetration of hair-fine needles into the skin to promote physiological healing. It has proved to be successful in treating several dermatological conditions, including AD. The practice is gaining worldwide attention, with around 3 million adults in the United States using acupuncture in 2007.5 According to findings of a systematic review of 8 randomized control trials, acupuncture might be more effective than conventional medicine in relieving global symptoms of atopic eczema.6
Phytotherapy: Phytotherapy uses herbs, plants, and plant extracts to manage the disease. Herbal medicines, in topical as well as oral form, are gaining traction in the treatment of AD. They generally have anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects. A review conducted in 2020 showed promising results of herbal medicine as both monotherapy and adjunctive therapy in treating AD. Regarding efficacy and symptom relief, herbal medicine was found to be more effective than conventional medicine.7
Aromatherapy: Aromatherapy, using essential oils distilled from plants, is used to treat various disorders, such as stress, anxiety, and dermatological conditions. It is commonly used in combination with other nontraditional therapies. The essential oils in this therapy are administered to the body in various ways, including via direct massage, inhalation, or distillation in baths.8
Hypnotherapy: Hypnosis has increasingly been used in medicine to manage pain and anxiety. Because stress plays a vital role in aggravating symptoms and triggering flare-ups of AD, hypnotherapy can help improve some of the disease symptoms. Findings from a study published in the International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hypnosis showed hypnosis to be an effective treatment option for AD. The data further demonstrated that hypnosis could be used in patients as an alternative treatment option to systemic therapies.9
Climatotherapy: Climatotherapy has been indicated for patients with atopic eczema for many years. This form of therapy involves a combination of swimming and sunbathing in the sea for a few weeks. The Dead Sea basin is known as a natural treatment center for patients with dermatological and rheumatic conditions. Results of a scientific study highlight a temporal shift in the skin of patients with AD after exposure to Dead Sea climatotherapy. The findings further elucidate that climate can serve as a potential therapy for patients with AD by influencing the development and maintenance of personal microbiomes.10
Tuina: Tuina is a TCM therapy involving manual manipulation of soft body tissues to enhance health and well-being. According to data from a systematic review conducted in 2019, tuina massage therapy is an effective treatment option in improving symptoms and reducing relapse rates among children younger than 14 years of age. It has also been reported that tuina, either alone or in combination with other treatment options, may successfully improve common signs and symptoms of AD, including skin lesions, itchiness, edema, and papules.11
Diet and supplements: It is a common myth among patients with AD that avoiding certain foods may prevent allergic reactions and flare-ups of the disease. However, making dietary changes can help reduce inflammation, boost the immune system, and improve some of the symptoms associated with AD. Some common vitamins and supplements used by patients with AD to manage their symptoms include vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin D, antioxidants, zinc, fish oil, prebiotics and probiotics, selenium, CBD and melatonin.12 Data from a study published in the American Journal of Clinical Dermatology revealed the role of vitamin D supplements in reducing AD severity.13
Relaxation techniques: Patients with AD are prone to anxiety and stress, which may serve as a triggering factor and can exacerbate the situation. It is crucial to address these factors and promote stress management. Some of the common relaxation techniques used among patients with AD to promote physical and mental well-being include meditation, yoga, breathing exercises, tai chi, and Reiki.8
Holistic medicine aims to address the overall well-being of patients, which requires greater teamwork and integration in the care chain. Although Western medicine has proved beneficial in treating symptoms, taking a holistic approach may help improve patients’ overall health. However, evaluating all benefits and risks associated with the therapy before prescribing any holistic treatment is imperative.
References
- Stanway A, Jarrett P. Atopic dermatitis. DermNet. Accessed November 11, 2022. https://dermnetnz.org/topics/atopic-dermatitis
- Chew YL. The beneficial properties of virgin coconut oil in management of atopic dermatitis. Pharmacogn Rev. 2019;13(25):24. doi:10.4103/phrev.phrev_29_18
- Varma SR, Sivaprakasam TO, Arumugam I, et al. In vitro anti-inflammatory and skin protective properties of Virgin coconut oil. J Tradit Complement Med. 2018;9(1):5-14. doi:10.1016/j.jtcme.2017.06.012
- Goddard AL, Lio PA. Alternative, complementary, and forgotten remedies for atopic dermatitis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:676897. doi:10.1155/2015/676897
- van den Berg-Wolf M, Burgoon T. Acupuncture and cutaneous medicine: is it effective? Med Acupunct. 2017;29(5):269-275. doi:10.1089/acu.2017.1227
- Jiao R, Yang Z, Wang Y, Zhou J, Zeng Y, Liu Z. The effectiveness and safety of acupuncture for patients with atopic eczema: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acupunct Med. 2020;38(1):3-14. doi:10.1177/0964528419871058
- Kwon CY, Lee B, Kim S, Lee J, Park M, Kim N. Effectiveness and safety of herbal medicine for atopic dermatitis: an overview of systematic reviews. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:4140692. doi:10.1155/2020/4140692
- Jadotte YT, Santer M, Vakirlis E, et al. Complementary and alternative medicine treatments for atopic eczema. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;2017(9):CD010938. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010938.pub2
- Delaitre L, Denis J, Maillard H. Hypnosis in treatment of atopic dermatitis: a clinical study. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 2020;68(4):412-418. doi:10.1080/00207144.2020.1788391
- Brandwein M, Fuks G, Israel A, et al. Skin microbiome compositional changes in atopic dermatitis accompany Dead Sea climatotherapy. Photochem Photobiol. 2019;95(6):1446-1453. Published correction appears in Photochem Photobiol. 2020;96(2):450.
- Lu C, Jin X, Wu D, Zhu S, Lai L, Liu J. Tuina for treatment of atopic eczema in children under 14 years: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. J Trad Chin Med Sci. 2019;6(1):13-25. doi:10.1016/j.jtcms.2018.12.006
- Can natural treatments help manage your eczema? National Eczema Association. October 16, 2022. https://nationaleczema.org/eczema/treatment/complementary-and-alternative. Accessed November 10, 2022
- Ng JC, Yew YW. Effect of vitamin D serum levels and supplementation on atopic dermatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23(3):267-275. doi:10.1007/s40257-022-00677
Articles in this issue
about 3 years ago
Cost-Effectiveness of Treating Advanced Melanomaabout 3 years ago
Q&A: Muneeb Shah, DO, Discusses What it Means to Have Healthy Skinabout 3 years ago
2022 Top Trends and What’s Next in Dermatologyabout 3 years ago
Pulsed Dye Lasers for Cosmetic Proceduresabout 3 years ago
Top Meeting Takeaways From the Fall Clinical Conferenceabout 3 years ago
Was It Marketing or Was It Misrepresentation?about 3 years ago
Treatment of Plaque Psoriasis in Childrenabout 3 years ago
A Conversation About JAK Inhibitors in Atopic Dermatitisabout 3 years ago
All You Need to Know About Back AcneNewsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.