Chemists try to mimic natural moisturizing factor
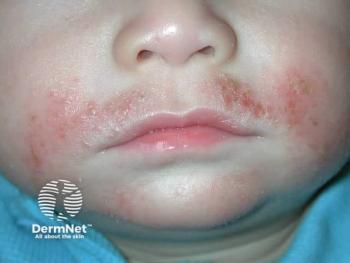
For years, cosmetic chemists have been looking for the mechanism whereby the skin remains naturally moisturized, and it has recently been identified.
Q. What is the NMF? How does it affect the skin?
A. NMF stands for natural moisturizing factor. For years, cosmetic chemists have been looking for the mechanism whereby the skin remains naturally moisturized. Certainly, there must be a chemical composition that the body uses to keep the skin from dehydrating. This mysterious substance was dubbed the natural moisturizing factor and recently its identity has been discovered.
It is now known that profilaggrin in the living epidermis is broken down to filaggrin as the keratinocytes mature in their journey from the basal cell layer to the stratum corneum. Filaggrin is an important component giving the epidermis mechanical stability. As the keratinocytes reach the upper epidermis, this filaggrin is broken down with protease enzymes to create the natural moisturizing factor necessary to regulate skin water content and maintain barrier function. The constituents of the natural moisturizing factor are urea, lactic acid, amino acids, pyrrolidone carboxylic acid, and inorganic salts. Cosmetic chemists have tried to mimic this combination in some of the newer therapeutic moisturizers in the marketplace. Indeed, these NMF moisturizers do perform better in clinical testing, especially on diseased skin.
More conundrums
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.