Barrier Function and Atopic Dermatitis
A dermatology expert reviews the role of barrier function in AD and outlines available treatments, emphasizing the importance of moisturizing and rapid options when appropriate, as well as the efficacy of rapid systemic treatments in patients when appropriate.
Episodes in this series

This is a video synopsis of a discussion involving Alexandra Golant, MD, Assistant Professor at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, focusing on barrier dysfunction in atopic dermatitis (AD) and its implications for treatment.
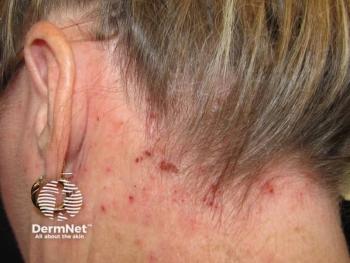
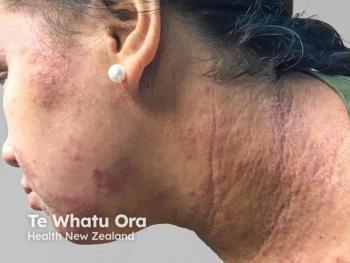
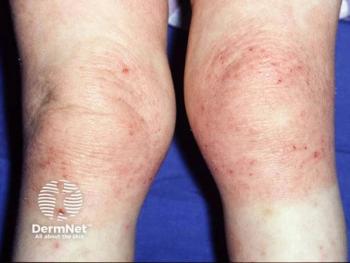
Dr. Golant underscores the significance of barrier dysfunction in understanding the pathophysiology of AD, emphasizing the interplay between impaired skin barrier function and skewed inflammatory responses. In individuals with AD, particularly those with hand and foot involvement, the compromised barrier exacerbates symptoms when exposed to irritants and allergens.
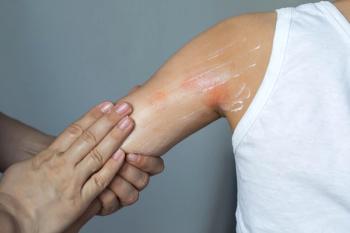
Addressing skin barrier function is crucial in managing AD, especially in patients with hand and foot involvement. Dr. Golant stresses the importance of patient education on gentle skincare practices aimed at restoring the skin barrier through the use of emollients and moisturizers. While mild cases may respond to improved skincare alone, moderate to severe cases often require additional topical or systemic therapies.
Practicality is key in treatment recommendations, especially for patients with disease affecting the hands and feet. Dr. Golant emphasizes tailoring treatment regimens to patients' lifestyles to ensure compliance. Recommending practical skincare routines that fit into patients' daily lives improves adherence and enhances treatment effectiveness.
In summary, Dr. Golant highlights the central role of barrier dysfunction in AD and the importance of practical treatment approaches tailored to individual patient needs, particularly in cases involving hand and foot involvement. Addressing barrier repair through skincare practices forms the basis of effective management strategies for AD.
Video synopsis is AI-generated and reviewed by Dermatology Times® editorial staff.
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.