|Slideshows|September 14, 2018
Must read studies on atopic dermatitis
Author(s)Dermatology Times Staff
Listen
0:00 / 0:00
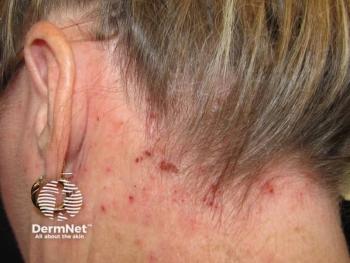
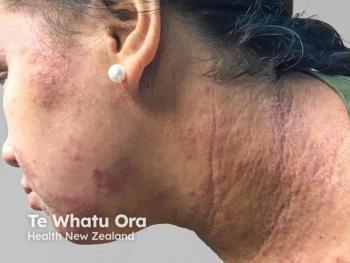
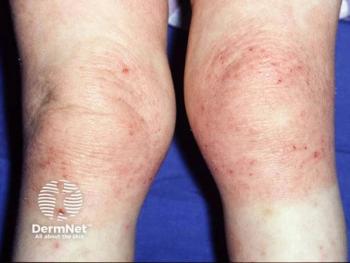
In this slideshow, we highlight some of the most innovative and important clinical advances in the treatment of atopic dermatitis.
Advertisement
In this slideshow, we highlight some of the most innovative and important clinical advances in the treatment of atopic dermatitis.
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.
Advertisement
Latest CME
Advertisement
Advertisement