Study Explores Efficacy of Topical MTX
In the past, there were many efforts to develop topical MTX, but the major obstacle was its physicochemical properties.
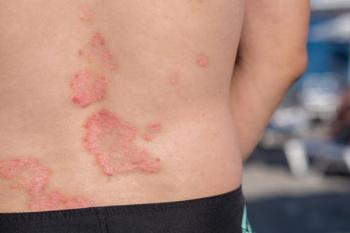
Methotrexate (MTX) has been the cornerstone conventional systemic treatment for moderate to severe psoriasis for a long time. In fact, the drug was first approved for psoriasis treatment by the USDA in 1972 and remains in the latest guideline as the primary treatment for moderate to severe psoriasis.
MTX is hydrophilic whereas the lipid constituents of the stratum corneum are lipophilic, which limits the permeation of hydrophilic molecules. Nowadays, several drug delivery techniques—such as chemical and/or physical penetration enhancers, intralesional injection and nanocarrier drug-delivery systems—have been investigated and used to overcome the problem of the low skin-penetration ability of MTX.
A new study1 led by dermatologists at Siriraj Hospital in Thailand reviewed the efficacy of topical MTX.
“We hoped that this study will benefit researchers worldwide who are pursuing the development of the most suitable formations of topical MTX,” said lead author Chayada Chaiyabutr, MD, a dermatologist in the Department of Dermatology at Siriraj Hospital.
While past studies have examined drug delivery techniques including chemical and/or physical penetration enhancers, intralesional injection and nanocarrier drug-delivery system, many of those investigations have varied between no benefits to a marked clinical improvement. Chaiyabutr explains the objective of this study was to systematically review the efficacy of topical MTX focusing on new drug-delivery systems and intralesional MTX for psoriasis.
The researchers reviewed Embase and Medline databases, searched from inception to July 2022, using keywords related to “topical MTX,” “intralesional MTX” and “psoriasis.”
“To be considered for inclusion, studies had to investigate the anti-psoriatic efficacy of topical and/or intralesional MTX in psoriasis patients or an animal induced-mouse model of psoriasis,” Chaiyabutr said. “In all, 46 articles were retrieved.”
When examining topical plain MTX in aqueous cream or gel, the topical plain MTX was produced by dissolving MTX in an aqueous cream or gel without using any enhancers or drug-assisted technology. The authors concluded that, while the formulation was well tolerated, it was not very effective and the MTX gel did not induce any systemic or local adverse effects.
The next review was of topical MTX with chemical enhancer, one of the most convenient ways to facilitate the penetration of drugs into the stratum corneum as it disrupts the stratum corneum and then decreases the skin barrier resistance.
The researchers looked at four studies about this, and while 75 percent revealed clinical benefits from the use of topical MTX with a chemical enhancer, Chaiyabutr notes there are some difficulties associated with its use in practice.
“As the macromolecular weight of MTX is quite high, a high concentration of chemical enhancer is needed to permeate the skin effectively, resulting in skin irritation,” she said.
Other past studies that were reviewed included opical MTX with Diode Laser, Topical MTX with Fractional Laser, Topical MTX with Photodynamic Therapy, Topical MTX with Iontophoresis, Topical MTX with Microneedle Patches and Intralesional MTX
A main takeaway is that efficacy of plain MTX as an aqueous cream or gel and of topical MTX with chemical enhancers do not seem promising due to their difficulty achieving skin penetration and their high risk of skin irritation.
“Nanoscale-based drug delivery—with and without physical enhancers such as an ablative laser or microneedle patches—are an interesting option,” Chaiyabutr says. “Most nanoscale drug delivery systems have shown good efficacy in animal models of psoriasis. However, data on the use of those techniques in patients with psoriasis are scarce.”
Looking ahead, the authors note further studies in large number of human psoriasis patients are needed to establish the most effective drug delivery system for psoriasis treatment.
“There were several interesting MTX delivery technique for using in psoriasis. Many of them demonstrated good efficacy in animal model-induced psoriasis,” Chaiyabutr said. “This review will benefit researchers worldwide who are pursuing the development of the most suitable formations of topical MTX.”
Reference
1. Chaiyabutr C, Punnakitikashem P, Silpa-archa N, Wongpraprarut C, Chularojanamontri L. The Anti-Psoriatic Efficacy and Safety Profile of Topical and Intralesional Methotrexate: A Literature Review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15:2253-2274
https://doi.org/10.2147/CCID.S380218
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.