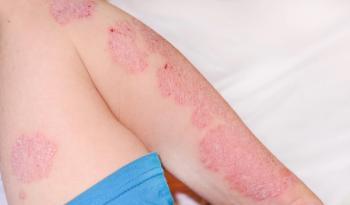
A recent study1 published in the International Journal of STD & AIDS found that 4 male patients with concomitant psoriasis and HIV infection experienced treatment efficacy with risankizumab.
According to study authors Orsini et al, the estimated prevalence of psoriasis among individuals with HIV (PLHIV) is comparable to that of the general population.
“In the context of HIV infection, the onset or worsening of psoriasis could reflect the direct impact of viral infection on cytokine balance and the cell-mediated inflammatory processes associated with the immune regeneration following antiretroviral therapy,” study authors wrote.
Citing limited treatment capabilities due to the immune-suppressive nature of common systemic drugs for HIV and limited data on interleukin(IL)-23 inhibitors and their efficacy in PLHIV, investigators sought to explore the safety and efficacy of risankizumab in patients with concomitant psoriasis and HIV infection.
Key Takeaways
- The study found that risankizumab was effective in improving psoriasis symptoms in these patients without observable adverse effects or viral reactivation.
- Despite promising results, the researchers emphasized the need for more extensive prospective studies to further evaluate the safety and efficacy of risankizumab and other treatments for psoriasis in people living with HIV.
Study authors described 4 distinct patient cases of male PLHIV.
In the first patient, 150 mg of risankizumab was prescribed at week 0, 4, and every 12 weeks thereafter. The patient achieved complete skin clearance as early as week 16. The second patient demonstrated a successful treatment response at the same 16-week measure.
A third PLHIV achieved a Psoriasis Area and Severity (PASI) score of 1 after week 16. The fourth and final PLHIV achieved complete skin clearance at week 16.
In all 4 patients, none experienced observable adverse effects or viral reactivation as a result of treatment with risankizumab. The drug was well-tolerated in each patient.
Despite the outcomes of this study of risankizumab in PLHIV, researchers said there is still significantly limited data on the treatment of psoriasis in PLHIV. In particular, they noted that TNF-alfa- specific data and research in PLHIV with psoriasis is limited.
“There is an urgent need to find safe and effective treatments for PLHIV with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis,” wrote Orsini et al. “In our experience, we choose to prescribe risankizumab because of its safety profile, high effectiveness, and the availability of data on interleukin inhibitors in the management of patients with psoriasis and chronic infection. However, more extensive prospective studies are strongly needed to support our findings.”
Reference
- Orsini D, Maramao FS, Gargiulo L, et al. Effectiveness and safety of risankizumab in HIV patients with psoriasis: A case series [published online ahead of print, 2023 Sep 10]. Int J STD AIDS. 2023;9564624231199510. doi:10.1177/09564624231199510