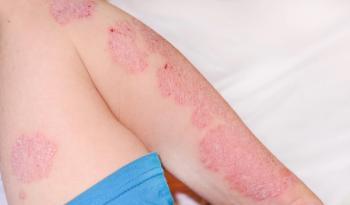
A recent study1 published by Skin Research and Technology found that endo-radiofrequency was both safe and effective in treating patients with refractory hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) of the axilla.
Investigators cited a lack of studies exploring the ability of radiofrequency intervention to safely and effectively destroy nodulocytic clinical lesions and remodel collagen fibers in patients with HS. They noted that radiofrequency has been used for remodeling collagen fibers and impacting sebaceous glands to treat acne vulgaris.
The non-randomized, prospective, and single-blinded study was conducted at a single dermatology clinic and included teen and adult patients between the ages of 15 and 65 years old with refractory HS; these patients had been referred to the dermatology clinic where the study was conducted between October and December 2021. All patients (n=10) had received a clinical HS diagnosis and had reported dissatisfaction with previous treatment modalities.
Patients who were pregnant or breastfeeding, had an active skin or systemic infection, a family history of bleeding or coagulant diseases, a history of malignancy or immunosuppression (including history of chemotherapy), or were actively taking coagulants, were excluded from participation. Additionally, patients with a less than 10 blood hemoglobin or less than 150,000 platelets were ineligible to participate.
Key Takeaways
- The study found that endo-radiofrequency was a safe and effective treatment option for patients with refractory hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) of the axilla.
- Researchers highlighted the lack of studies exploring the potential of radiofrequency intervention to effectively target nodulocytic clinical lesions and remodel collagen fibers in HS patients, despite its successful use in treating conditions like acne vulgaris.
- After undergoing treatment sessions, 80% of participants reported moderate to excellent levels of treatment satisfaction, while the recurrence of the disease decreased in the follow-up period.
Investigators conducted a pre-treatment analysis, including the collection of demographic and clinical data, including HS physicians’ global assessment (HS-PGA) scores.
During each of the 3 treatment sessions, all patients’ axilla were disinfected, dried, and anesthetized with lidocaine. The areas were then treated with a radiofrequency device (Aphrodite, 4 MHZ, monopolar, 60 W and 1 KΩ).
Levels of patient satisfaction were collected 3 months post-treatment, and investigators determined recurrence of disease at a 6-months post treatment follow-up.
Three months after undergoing treatment, 80% of participants (n=8) reported a moderate, good, or excellent level of treatment satisfaction. The same number of participants also reported treatment tolerability. During this first follow-up, 4 participants met recurrence criteria. However, during the second follow-up, only 2 participants had met recurrence criteria.
“RF [radiofrequency] is a safe and effective therapeutic approach for controlling axillary HS,” wrote study authors Behrangi et al. “However, to prevent the recurrence, periodic therapy sessions are needed.”
Reference
- Behrangi E, Atefi N, Mireshghollah P, et al. The efficacy and safety of endo‐radiofrequency for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa. Skin Res Technol. 2023;29(9). doi:10.1111/srt.13450